Fungal folliculitis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Majocchi_granuloma_new_image_in_2019.jpg | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 22:05, 16 February 2025
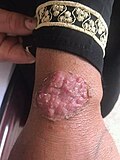
Fungal folliculitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the hair follicles due to a fungal infection. It is a common dermatological issue that can affect individuals of all ages.
Causes
Fungal folliculitis is primarily caused by the overgrowth of fungi, particularly the yeast-like fungus Candida. Other fungi that can cause this condition include Dermatophytes and Malassezia. These fungi are usually present on the skin but can cause infection when they multiply excessively.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of fungal folliculitis include:
- Red, inflamed hair follicles
- Itching or discomfort in the affected area
- Pus-filled blisters around the hair follicles
- Hair loss in severe cases
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of fungal folliculitis is typically made through a physical examination and a review of the patient's medical history. In some cases, a skin scraping or biopsy may be performed for laboratory analysis to confirm the presence of fungi.
Treatment
Treatment for fungal folliculitis usually involves the use of antifungal medications, either topical or oral, depending on the severity of the condition. In some cases, the affected hair may need to be removed to allow the skin to heal.
Prevention
Prevention strategies for fungal folliculitis include maintaining good personal hygiene, avoiding sharing personal items like towels and razors, and keeping the skin dry and clean.