Trichomonas vaginalis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A protozoan parasite causing trichomoniasis}} | |||
'''Trichomonas vaginalis''' is a [[protozoan]] [[parasite]] and the causative agent of [[trichomoniasis]], a common [[sexually transmitted infection]] (STI) in humans. It is a flagellated anaerobic organism that primarily infects the urogenital tract. | |||
== | ==Morphology== | ||
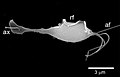
''Trichomonas vaginalis'' is a pear-shaped organism with five flagella, four of which are anterior and one is posterior, aiding in its motility. It has an undulating membrane that extends about two-thirds of its body length. The organism is approximately 7 to 23 micrometers in length and 5 to 15 micrometers in width. | |||
==Life Cycle== | |||
The life cycle of ''Trichomonas vaginalis'' is relatively simple, consisting of a trophozoite stage only. It does not form cysts. The trophozoites multiply by binary fission and are transmitted from person to person primarily through sexual contact. | |||
==Pathogenesis== | |||
''Trichomonas vaginalis'' infects the urogenital tract, causing inflammation and irritation. In women, it can lead to vaginitis, characterized by a frothy, yellow-green vaginal discharge with a strong odor, itching, and discomfort during urination or intercourse. In men, the infection is often asymptomatic but can cause urethritis. | |||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of | Diagnosis of ''Trichomonas vaginalis'' infection is typically made through microscopic examination of vaginal or urethral swabs. The organism can be identified by its characteristic motility. Other diagnostic methods include culture, antigen detection, and nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs). | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
The treatment for trichomoniasis | The standard treatment for trichomoniasis is [[metronidazole]] or [[tinidazole]], which are effective in eradicating the infection. It is important for sexual partners to be treated simultaneously to prevent reinfection. | ||
==Epidemiology== | |||
''Trichomonas vaginalis'' is one of the most common non-viral STIs worldwide. It affects millions of people annually, with higher prevalence rates in women than in men. The infection is more common in certain populations, including those with multiple sexual partners and those with other STIs. | |||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
Preventive measures | Preventive measures include practicing safe sex, using condoms, and regular STI screenings. Educating individuals about the transmission and symptoms of trichomoniasis can also help reduce the spread of the infection. | ||
== | ==Related pages== | ||
* [[Trichomoniasis]] | |||
* [[Sexually transmitted infection]] | |||
* [[Protozoan]] | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist}} | |||
== | ==Gallery== | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Trichomonas_vaginalis_observed_by_scanning_electron_microscopy.jpg|''Trichomonas vaginalis'' observed by scanning electron microscopy | |||
File:Trichomonas_vaginalis_(20).png|''Trichomonas vaginalis'' image | |||
File:Trichomonas_vaginalis_(21).JPG|''Trichomonas vaginalis'' under a microscope | |||
File:Trichomonas_vaginalis_(02).png|''Trichomonas vaginalis'' illustration | |||
File:Trichomonas_vaginalis_infection_-_phase_contrast.mpg|''Trichomonas vaginalis'' infection video | |||
File:Pap_test_trichomonas.JPG|Pap test showing ''Trichomonas vaginalis'' | |||
File:Trichomonas_vaginalis.webm|''Trichomonas vaginalis'' video | |||
File:TV_in_Gram.jpg|''Trichomonas vaginalis'' in Gram stain | |||
File:Trichomonas_vaginalis_02.webm|''Trichomonas vaginalis'' video | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[Category:Parasitic protozoa]] | |||
[[Category:Sexually transmitted diseases and infections]] | [[Category:Sexually transmitted diseases and infections]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:37, 10 February 2025
A protozoan parasite causing trichomoniasis
Trichomonas vaginalis is a protozoan parasite and the causative agent of trichomoniasis, a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in humans. It is a flagellated anaerobic organism that primarily infects the urogenital tract.
Morphology[edit]
Trichomonas vaginalis is a pear-shaped organism with five flagella, four of which are anterior and one is posterior, aiding in its motility. It has an undulating membrane that extends about two-thirds of its body length. The organism is approximately 7 to 23 micrometers in length and 5 to 15 micrometers in width.
Life Cycle[edit]
The life cycle of Trichomonas vaginalis is relatively simple, consisting of a trophozoite stage only. It does not form cysts. The trophozoites multiply by binary fission and are transmitted from person to person primarily through sexual contact.
Pathogenesis[edit]
Trichomonas vaginalis infects the urogenital tract, causing inflammation and irritation. In women, it can lead to vaginitis, characterized by a frothy, yellow-green vaginal discharge with a strong odor, itching, and discomfort during urination or intercourse. In men, the infection is often asymptomatic but can cause urethritis.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis infection is typically made through microscopic examination of vaginal or urethral swabs. The organism can be identified by its characteristic motility. Other diagnostic methods include culture, antigen detection, and nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs).
Treatment[edit]
The standard treatment for trichomoniasis is metronidazole or tinidazole, which are effective in eradicating the infection. It is important for sexual partners to be treated simultaneously to prevent reinfection.
Epidemiology[edit]
Trichomonas vaginalis is one of the most common non-viral STIs worldwide. It affects millions of people annually, with higher prevalence rates in women than in men. The infection is more common in certain populations, including those with multiple sexual partners and those with other STIs.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures include practicing safe sex, using condoms, and regular STI screenings. Educating individuals about the transmission and symptoms of trichomoniasis can also help reduce the spread of the infection.
Related pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
Gallery[edit]
-
Trichomonas vaginalis observed by scanning electron microscopy
-
Trichomonas vaginalis image
-
Trichomonas vaginalis under a microscope
-
Trichomonas vaginalis illustration
-
Trichomonas vaginalis infection video
-
Pap test showing Trichomonas vaginalis
-
Trichomonas vaginalis video
-
Trichomonas vaginalis in Gram stain
-
Trichomonas vaginalis video