Square: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Five Squared.svg|thumb|Five Squared|right]] [[File:Square equation plot.svg|thumb|Square equation plot|left]] [[File:Straight Square Inscribed in a Circle 240px.gif|thumb|Straight Square Inscribed in a Circle 240px.gif]] [[File:01-Quadrat-Seite-gegeben.gif|thumb|01-Quadrat-Seite-gegeben|right]] [[File:01-Quadrat-Diagonale-gegeben.gif|thumb|01-Quadrat-Diagonale-gegeben|right]] [[File:Symmetries of square.svg|thumb|Symmetries of square.svg]] {{Short description|Geometric shape with four equal sides}} | [[Image:Five Squared.svg|thumb|Five Squared|right]] [[File:Square equation plot.svg|thumb|Square equation plot|left]] [[File:Straight Square Inscribed in a Circle 240px.gif|thumb|Straight Square Inscribed in a Circle 240px.gif]] [[File:01-Quadrat-Seite-gegeben.gif|thumb|01-Quadrat-Seite-gegeben|right]] [[File:01-Quadrat-Diagonale-gegeben.gif|thumb|01-Quadrat-Diagonale-gegeben|right]] [[File:Symmetries of square.svg|thumb|Symmetries of square.svg]] {{Short description|Geometric shape with four equal sides}} | ||
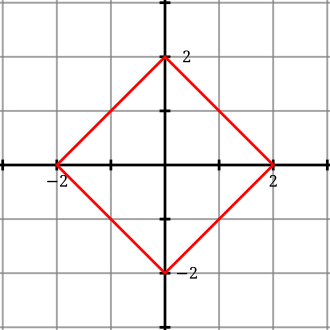
A '''square''' is a [[regular polygon]] with four equal sides and four equal [[angle]]s of 90 degrees each. It is a type of [[quadrilateral]] and a special case of a [[rectangle]] and a [[rhombus]]. | A '''square''' is a [[regular polygon]] with four equal sides and four equal [[angle]]s of 90 degrees each. It is a type of [[quadrilateral]] and a special case of a [[rectangle]] and a [[rhombus]]. | ||
==Properties== | ==Properties== | ||
Latest revision as of 22:46, 5 January 2025




Geometric shape with four equal sides
A square is a regular polygon with four equal sides and four equal angles of 90 degrees each. It is a type of quadrilateral and a special case of a rectangle and a rhombus.
Properties[edit]
A square has several key properties:
- All four sides are of equal length.
- All four angles are right angles (90 degrees).
- The diagonals of a square are equal in length and bisect each other at right angles.
- The diagonals also bisect the angles of the square.
- The square has a high degree of symmetry, with four lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry of order 4.
Formulas[edit]
The following formulas are used to calculate various properties of a square:
- Perimeter: \( P = 4a \), where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Area: \( A = a^2 \).
- Diagonal: \( d = a\sqrt{2} \).
Geometric Constructions[edit]
A square can be constructed using a compass and straightedge: 1. Draw a line segment of the desired length. 2. Construct a perpendicular bisector of the line segment. 3. Use the compass to mark off equal lengths along the perpendicular bisector. 4. Connect the endpoints to form a square.
Applications[edit]
Squares are used in various fields such as geometry, architecture, and art. They are fundamental in tessellations and are often used in design and engineering due to their symmetry and simplicity.
Related Shapes[edit]
- Rectangle: A quadrilateral with opposite sides equal and all angles 90 degrees.
- Rhombus: A quadrilateral with all sides equal but not necessarily all angles 90 degrees.
- Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and equal in length.
- Quadrilateral: A polygon with four sides.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>

This article is a geometry-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!