Busch fracture: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Busch fracture | |||
| image = [[File:Malletfinger.jpg|left|thumb|Mallet finger, a type of [[avulsion fracture]]]] | |||
| caption = Mallet finger, a type of avulsion fracture | |||
| synonyms = Mallet finger fracture | |||
| specialty = [[Orthopedic surgery]] | |||
| symptoms = Pain, swelling, inability to extend the [[distal phalanx]] | |||
| complications = [[Chronic pain]], [[arthritis]] | |||
| onset = Sudden, following trauma | |||
| duration = Varies, weeks to months | |||
| causes = [[Trauma]] to the [[finger]] | |||
| risks = Sports, manual labor | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[X-ray]] | |||
| differential = [[Jersey finger]], [[finger dislocation]] | |||
| treatment = [[Splinting]], [[surgery]] | |||
| medication = [[NSAIDs]] for pain | |||
| prognosis = Good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in sports injuries | |||
}} | |||
== Busch Fracture == | == Busch Fracture == | ||
A '''Busch fracture''' is a specific type of [[avulsion fracture]] that occurs at the base of the [[distal phalanx]] of a finger. This injury is often associated with a condition known as [[mallet finger]], which results from the disruption of the [[extensor tendon]] at the distal interphalangeal joint. | A '''Busch fracture''' is a specific type of [[avulsion fracture]] that occurs at the base of the [[distal phalanx]] of a finger. This injury is often associated with a condition known as [[mallet finger]], which results from the disruption of the [[extensor tendon]] at the distal interphalangeal joint. | ||
[[File:Avulsion_fracture_xray_finger.jpg|An X-ray showing an avulsion fracture of the finger|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Avulsion_fracture_xray_finger.jpg|An X-ray showing an avulsion fracture of the finger|thumb | |||
=== Mechanism of Injury === | === Mechanism of Injury === | ||
The Busch fracture typically occurs when an external force is applied to the tip of the finger, causing the distal phalanx to flex suddenly while the extensor tendon is under tension. This forceful flexion can lead to the avulsion of a small fragment of bone at the tendon insertion site. The injury is common in sports such as [[baseball]], [[basketball]], and [[volleyball]], where the fingers are frequently exposed to sudden impacts. | The Busch fracture typically occurs when an external force is applied to the tip of the finger, causing the distal phalanx to flex suddenly while the extensor tendon is under tension. This forceful flexion can lead to the avulsion of a small fragment of bone at the tendon insertion site. The injury is common in sports such as [[baseball]], [[basketball]], and [[volleyball]], where the fingers are frequently exposed to sudden impacts. | ||
[[File:Mallet_finger_mechanism.svg|Diagram illustrating the mechanism of mallet finger injury|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Mallet_finger_mechanism.svg|Diagram illustrating the mechanism of mallet finger injury|thumb | |||
=== Clinical Presentation === | === Clinical Presentation === | ||
Patients with a Busch fracture typically present with pain, swelling, and an inability to extend the distal phalanx of the affected finger. The finger may appear to droop at the distal interphalangeal joint, a characteristic sign of mallet finger. The injury is often accompanied by tenderness at the site of the fracture. | Patients with a Busch fracture typically present with pain, swelling, and an inability to extend the distal phalanx of the affected finger. The finger may appear to droop at the distal interphalangeal joint, a characteristic sign of mallet finger. The injury is often accompanied by tenderness at the site of the fracture. | ||
=== Diagnosis === | === Diagnosis === | ||
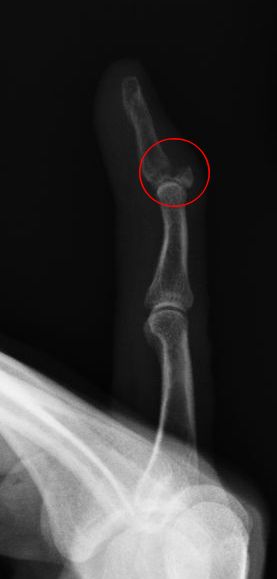
Diagnosis of a Busch fracture is primarily based on clinical examination and confirmed with [[radiography]]. An X-ray of the affected finger will reveal the avulsion fracture at the base of the distal phalanx. It is important to assess the size of the avulsed fragment and the degree of joint subluxation, as these factors can influence treatment decisions. | Diagnosis of a Busch fracture is primarily based on clinical examination and confirmed with [[radiography]]. An X-ray of the affected finger will reveal the avulsion fracture at the base of the distal phalanx. It is important to assess the size of the avulsed fragment and the degree of joint subluxation, as these factors can influence treatment decisions. | ||
=== Treatment === | === Treatment === | ||
The treatment of a Busch fracture depends on the size of the avulsed fragment and the degree of joint involvement. Non-surgical management is often preferred, especially for small fractures without significant joint subluxation. This typically involves splinting the distal interphalangeal joint in extension for a period of 6 to 8 weeks to allow for proper healing of the tendon and bone. | The treatment of a Busch fracture depends on the size of the avulsed fragment and the degree of joint involvement. Non-surgical management is often preferred, especially for small fractures without significant joint subluxation. This typically involves splinting the distal interphalangeal joint in extension for a period of 6 to 8 weeks to allow for proper healing of the tendon and bone. | ||
[[File:Malletfinger.jpg|A clinical image of a mallet finger injury|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Malletfinger.jpg|A clinical image of a mallet finger injury|thumb | |||
In cases where the fracture fragment is large or there is significant joint subluxation, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options include open reduction and internal fixation or the use of specialized splints to maintain joint alignment during healing. | In cases where the fracture fragment is large or there is significant joint subluxation, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options include open reduction and internal fixation or the use of specialized splints to maintain joint alignment during healing. | ||
=== Prognosis === | === Prognosis === | ||
With appropriate treatment, most patients with a Busch fracture can expect a good functional outcome. However, some may experience residual stiffness or a slight extension lag at the distal interphalangeal joint. Early diagnosis and adherence to treatment protocols are crucial for optimal recovery. | With appropriate treatment, most patients with a Busch fracture can expect a good functional outcome. However, some may experience residual stiffness or a slight extension lag at the distal interphalangeal joint. Early diagnosis and adherence to treatment protocols are crucial for optimal recovery. | ||
[[File:Mallet_Finger_Injury.jpg|A mallet finger injury showing the characteristic droop|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Mallet_Finger_Injury.jpg|A mallet finger injury showing the characteristic droop|thumb | == See also == | ||
== | |||
* [[Mallet finger]] | * [[Mallet finger]] | ||
* [[Avulsion fracture]] | * [[Avulsion fracture]] | ||
* [[Extensor tendon injuries]] | * [[Extensor tendon injuries]] | ||
{{Medical conditions}} | {{Medical conditions}} | ||
[[Category:Fractures]] | [[Category:Fractures]] | ||
[[Category:Hand injuries]] | [[Category:Hand injuries]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:05, 4 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Busch fracture | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Synonyms | Mallet finger fracture |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Orthopedic surgery |
| Symptoms | Pain, swelling, inability to extend the distal phalanx |
| Complications | Chronic pain, arthritis |
| Onset | Sudden, following trauma |
| Duration | Varies, weeks to months |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Trauma to the finger |
| Risks | Sports, manual labor |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, X-ray |
| Differential diagnosis | Jersey finger, finger dislocation |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Splinting, surgery |
| Medication | NSAIDs for pain |
| Prognosis | Good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common in sports injuries |
| Deaths | N/A |
Busch Fracture[edit]
A Busch fracture is a specific type of avulsion fracture that occurs at the base of the distal phalanx of a finger. This injury is often associated with a condition known as mallet finger, which results from the disruption of the extensor tendon at the distal interphalangeal joint.
Mechanism of Injury[edit]
The Busch fracture typically occurs when an external force is applied to the tip of the finger, causing the distal phalanx to flex suddenly while the extensor tendon is under tension. This forceful flexion can lead to the avulsion of a small fragment of bone at the tendon insertion site. The injury is common in sports such as baseball, basketball, and volleyball, where the fingers are frequently exposed to sudden impacts.

Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with a Busch fracture typically present with pain, swelling, and an inability to extend the distal phalanx of the affected finger. The finger may appear to droop at the distal interphalangeal joint, a characteristic sign of mallet finger. The injury is often accompanied by tenderness at the site of the fracture.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of a Busch fracture is primarily based on clinical examination and confirmed with radiography. An X-ray of the affected finger will reveal the avulsion fracture at the base of the distal phalanx. It is important to assess the size of the avulsed fragment and the degree of joint subluxation, as these factors can influence treatment decisions.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of a Busch fracture depends on the size of the avulsed fragment and the degree of joint involvement. Non-surgical management is often preferred, especially for small fractures without significant joint subluxation. This typically involves splinting the distal interphalangeal joint in extension for a period of 6 to 8 weeks to allow for proper healing of the tendon and bone.

In cases where the fracture fragment is large or there is significant joint subluxation, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options include open reduction and internal fixation or the use of specialized splints to maintain joint alignment during healing.
Prognosis[edit]
With appropriate treatment, most patients with a Busch fracture can expect a good functional outcome. However, some may experience residual stiffness or a slight extension lag at the distal interphalangeal joint. Early diagnosis and adherence to treatment protocols are crucial for optimal recovery.

See also[edit]