Memory improvement: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description| | {{Short description|Methods and techniques to enhance memory}} | ||
[[File:Hippocampus_small.gif|The hippocampus, a critical brain region for memory|thumb|right]] | |||
'''Memory improvement''' refers to techniques and strategies aimed at enhancing an individual's ability to encode, store, and retrieve information. Memory is a complex cognitive process that involves various brain regions, including the [[hippocampus]], [[prefrontal cortex]], and [[amygdala]]. Improving memory can be beneficial for academic performance, professional success, and overall quality of life. | |||
Memory is a complex cognitive process that involves | |||
==Techniques for Memory Improvement== | ==Techniques for Memory Improvement== | ||
There are several methods and strategies that individuals can employ to improve their memory. These techniques can be broadly categorized into lifestyle changes, cognitive exercises, and mnemonic devices. | |||
===Lifestyle Changes=== | |||
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in memory function. Key lifestyle changes that can enhance memory include: | |||
* '''Diet and Nutrition''': Consuming a balanced diet rich in [[omega-3 fatty acids]], [[antioxidants]], and [[vitamins]] can support brain health. Foods such as [[fish]], [[nuts]], and [[berries]] are particularly beneficial. | |||
* '''Exercise''': Regular physical activity increases blood flow to the brain and promotes the growth of new neurons, particularly in the hippocampus. | |||
* '''Sleep''': Adequate sleep is crucial for memory consolidation, the process by which short-term memories are transformed into long-term memories. | |||
* '''Stress Management''': Chronic stress can impair memory. Techniques such as [[meditation]], [[yoga]], and [[deep breathing]] can help reduce stress levels. | |||
[[File:Brain_animated_color_nevit.gif|The human brain, involved in memory processes|thumb|left]] | |||
===Cognitive Exercises=== | |||
Engaging in activities that challenge the brain can improve memory. These include: | |||
* '''Puzzles and Games''': Activities like [[crossword puzzles]], [[Sudoku]], and [[chess]] stimulate cognitive function. | |||
* '''Learning New Skills''': Acquiring new skills, such as learning a musical instrument or a new language, can enhance memory and cognitive flexibility. | |||
* '''Memory Training Programs''': Structured programs designed to improve specific memory skills can be effective. | |||
===Mnemonic Devices=== | ===Mnemonic Devices=== | ||
Mnemonic devices are techniques that aid in the retention and retrieval of information. Common mnemonic strategies include: | |||
* '''Acronyms and Acrostics''': Creating acronyms or acrostics to remember lists or sequences. | |||
* '''Visualization''': Associating information with vivid mental images. | |||
* '''Chunking''': Breaking down large pieces of information into smaller, manageable units. | |||
* '''Chunking''': Breaking down information into smaller, manageable units | |||
* '''Method of Loci''': Associating information with specific locations in a familiar environment. | |||
[[File:String_around_finger.jpg|A string around | |||
[[File:String_around_finger.jpg|A string tied around a finger, a traditional reminder technique|thumb|right]] | |||
==Memory and Aging== | ==Memory and Aging== | ||
As individuals age, memory can decline | |||
As individuals age, memory function can decline. However, engaging in memory improvement techniques can help mitigate age-related memory loss. Older adults are encouraged to maintain an active lifestyle, engage in social activities, and continue learning to preserve cognitive function. | |||
==Memory Disorders== | |||
Memory disorders, such as [[Alzheimer's disease]] and [[dementia]], significantly impact memory function. While memory improvement techniques cannot cure these conditions, they may help slow progression and improve quality of life. | |||
==Related Pages== | ==Related Pages== | ||
* [[Cognitive | |||
* [[Cognitive psychology]] | |||
* [[Neuroplasticity]] | * [[Neuroplasticity]] | ||
* [[Learning]] | * [[Learning]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Brain health]] | ||
[[File:Trataka.JPG|Trataka, a meditation technique for focus and memory|thumb|left]] | |||
==Conclusion== | |||
Memory improvement is a multifaceted approach that involves lifestyle changes, cognitive exercises, and mnemonic devices. By adopting these strategies, individuals can enhance their memory and cognitive abilities, leading to improved performance in various aspects of life. | |||
[[Category:Memory]] | [[Category:Memory]] | ||
[[Category:Cognitive psychology]] | [[Category:Cognitive psychology]] | ||
[[Category:Learning]] | [[Category:Learning]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:39, 6 March 2025
Methods and techniques to enhance memory
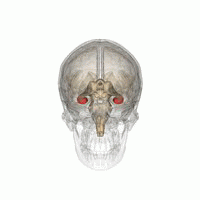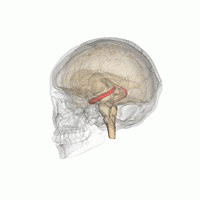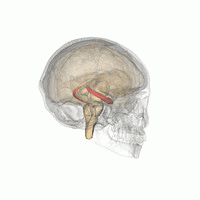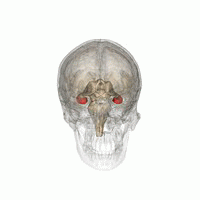
Memory improvement refers to techniques and strategies aimed at enhancing an individual's ability to encode, store, and retrieve information. Memory is a complex cognitive process that involves various brain regions, including the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and amygdala. Improving memory can be beneficial for academic performance, professional success, and overall quality of life.
Techniques for Memory Improvement[edit]
There are several methods and strategies that individuals can employ to improve their memory. These techniques can be broadly categorized into lifestyle changes, cognitive exercises, and mnemonic devices.
Lifestyle Changes[edit]
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in memory function. Key lifestyle changes that can enhance memory include:
- Diet and Nutrition: Consuming a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins can support brain health. Foods such as fish, nuts, and berries are particularly beneficial.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity increases blood flow to the brain and promotes the growth of new neurons, particularly in the hippocampus.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for memory consolidation, the process by which short-term memories are transformed into long-term memories.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can impair memory. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help reduce stress levels.
Cognitive Exercises[edit]
Engaging in activities that challenge the brain can improve memory. These include:
- Puzzles and Games: Activities like crossword puzzles, Sudoku, and chess stimulate cognitive function.
- Learning New Skills: Acquiring new skills, such as learning a musical instrument or a new language, can enhance memory and cognitive flexibility.
- Memory Training Programs: Structured programs designed to improve specific memory skills can be effective.
Mnemonic Devices[edit]
Mnemonic devices are techniques that aid in the retention and retrieval of information. Common mnemonic strategies include:
- Acronyms and Acrostics: Creating acronyms or acrostics to remember lists or sequences.
- Visualization: Associating information with vivid mental images.
- Chunking: Breaking down large pieces of information into smaller, manageable units.
- Method of Loci: Associating information with specific locations in a familiar environment.

Memory and Aging[edit]
As individuals age, memory function can decline. However, engaging in memory improvement techniques can help mitigate age-related memory loss. Older adults are encouraged to maintain an active lifestyle, engage in social activities, and continue learning to preserve cognitive function.
Memory Disorders[edit]
Memory disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease and dementia, significantly impact memory function. While memory improvement techniques cannot cure these conditions, they may help slow progression and improve quality of life.
Related Pages[edit]

Conclusion[edit]
Memory improvement is a multifaceted approach that involves lifestyle changes, cognitive exercises, and mnemonic devices. By adopting these strategies, individuals can enhance their memory and cognitive abilities, leading to improved performance in various aspects of life.