Hepatovirus: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
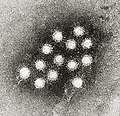
File:Hepatitis A virus 02.jpg|Hepatitis A virus | File:Hepatitis A virus 02.jpg|Hepatitis A virus | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 23:48, 16 March 2025
Hepatovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Picornaviridae. Humans and mammals serve as natural hosts. There are currently four species in this genus including the type species Hepatitis A virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: hepatitis A: an acute short-term disease.
Taxonomy[edit]
The genus Hepatovirus is part of the family Picornaviridae, a large family of viruses that also includes the Enterovirus and Rhinovirus genera, among others. The Hepatovirus genus includes the following species:
- Hepatovirus A
- Hepatovirus B
- Hepatovirus C
- Hepatovirus D
Structure[edit]
Viruses in Hepatovirus are non-enveloped, with icosahedral geometries, and T=pseudo3 symmetry. The diameter is around 30 nm. Genomes are linear and non-segmented, around 7.5kb in length.
Life Cycle[edit]
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the virus to host receptors, which mediates endocytosis. Replication follows the positive stranded RNA virus replication model. Positive stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. Translation takes place by ribosomal skipping, viral initiation, and ribosomal shifting. The virus exits the host cell by lysis, and viroporins. Humans and mammals serve as the natural host.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The most well-known and studied virus in the Hepatovirus genus is the Hepatitis A virus, which causes hepatitis A, an infectious disease of the liver. Hepatitis A is usually transmitted by the fecal-oral route, either by consumption of contaminated food or water or direct contact with an infectious person.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />