Molybdenum(V) fluoride: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{chem-stub}} | {{chem-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
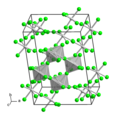
File:MoF5.png|MoF5 | File:MoF5.png|MoF5 | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:41, 17 March 2025
Molybdenum(V) fluoride', also known as molybdenum pentafluoride, is a chemical compound with the formula MoF5. This compound is of interest in the field of inorganic chemistry due to its unique properties and its use in various chemical reactions and applications.
Properties[edit]
Molybdenum(V) fluoride is characterized by its molecular structure, which consists of a molybdenum atom surrounded by five fluoride ions. This configuration leads to a trigonal bipyramidal geometry, a common structural motif for compounds with a central atom bonded to five other atoms. The compound is a solid under standard conditions and exhibits a high reactivity with water, releasing hydrogen fluoride (HF) upon contact.
Synthesis[edit]
The synthesis of MoF5 typically involves the direct fluorination of molybdenum or molybdenum compounds. One common method involves the reaction of molybdenum hexacarbonyl (Mo(CO)6) with fluorine gas (F2), which results in the formation of MoF5 and gaseous by-products. This process requires careful control of reaction conditions, including temperature and pressure, to ensure the selective production of MoF5.
Applications[edit]
Molybdenum(V) fluoride is used in various applications within the field of chemical synthesis and materials science. Its ability to act as a fluorinating agent makes it valuable in the preparation of fluorinated organic compounds. Additionally, MoF5 serves as a catalyst in certain types of chemical reactions, where it facilitates the transformation of substrates into desired products with high efficiency.
Safety and Handling[edit]
Due to its reactivity, especially with water, handling MoF5 requires strict safety precautions. The compound should be stored in airtight containers to prevent its reaction with atmospheric moisture. Protective equipment, including gloves and eye protection, is essential when working with this compound to avoid exposure to its toxic effects.
See Also[edit]
-
MoF5