Neuromedin N: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
{{neuropeptide-stub}} | {{neuropeptide-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
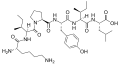
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Neuromedin_N.svg|Neuromedin N | File:Neuromedin_N.svg|Neuromedin N | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:46, 17 March 2025
Neuromedin N is a neuropeptide that is derived from the same precursor protein, neurotensin/neuromedin N precursor, as neurotensin. It is found in the central nervous system and in peripheral tissues, including the gastrointestinal tract and the hypothalamus. Neuromedin N has been implicated in a variety of physiological processes, including the regulation of gastrointestinal motility and hypothalamic functions.
Structure and Synthesis[edit]
Neuromedin N is a peptide composed of 36 amino acids. It is derived from the same precursor protein as neurotensin, a 13-amino acid peptide. The precursor protein is cleaved by prohormone convertase enzymes to produce the two peptides. The sequence of neuromedin N is highly conserved across species, suggesting that it plays a critical role in physiological processes.
Function[edit]
Neuromedin N has been shown to have a variety of physiological effects. In the gastrointestinal tract, it stimulates smooth muscle contraction and increases the secretion of pancreatic enzymes. In the hypothalamus, it influences the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone and thyrotropin-releasing hormone, and it has been implicated in the regulation of body temperature and food intake.
Neuromedin N also has neuroprotective effects. It has been shown to protect neurons from excitotoxicity, a process that leads to neuronal death in conditions such as stroke and neurodegenerative diseases.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Due to its wide range of physiological effects, neuromedin N has been implicated in a variety of diseases. It has been suggested to play a role in obesity, due to its effects on food intake. It may also be involved in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases, due to its neuroprotective effects.
Furthermore, neuromedin N has been found to be overexpressed in certain types of cancer, including small cell lung cancer and neuroendocrine tumors. This has led to the suggestion that it could be a potential target for cancer therapy.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
This neuropeptide-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
-
Neuromedin N