VEGFR-2 inhibitor: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{DISPLAYTITLE:VEGFR-2 inhibitor}} | ||
== | == Overview == | ||
[[File: | [[File:Lenvatinib_+_viðtaki.png|thumb|right|Lenvatinib binding to VEGFR-2]] | ||
VEGFR-2 | A '''VEGFR-2 inhibitor''' is a type of [[tyrosine kinase inhibitor]] that specifically targets the [[vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2]] (VEGFR-2). VEGFR-2 is a key receptor involved in the process of [[angiogenesis]], which is the formation of new blood vessels. Inhibiting VEGFR-2 can therefore be an effective strategy in the treatment of various [[cancer]]s, as it can reduce the blood supply to tumors, inhibiting their growth and metastasis. | ||
==Mechanism of Action== | == Mechanism of Action == | ||
VEGFR-2 inhibitors work by blocking the | [[File:Hvarfgangur.png|thumb|left|Mechanism of action of VEGFR-2 inhibitors]] | ||
VEGFR-2 inhibitors work by blocking the [[ATP]] binding site of the receptor, preventing its activation. This inhibition disrupts the downstream signaling pathways that promote endothelial cell proliferation and migration, which are essential for angiogenesis. By inhibiting these pathways, VEGFR-2 inhibitors can effectively reduce tumor vascularization and growth. | |||
== | == Chemical Classes == | ||
VEGFR-2 inhibitors belong to several chemical classes, each with distinct structural characteristics. Some of the notable classes include: | |||
== | === Quinazoline Derivatives === | ||
[[File:Quinazoline.png|thumb|right|Structure of a quinazoline derivative]] | |||
Quinazoline derivatives are a prominent class of VEGFR-2 inhibitors. These compounds typically feature a quinazoline core, which is crucial for their binding affinity to the receptor. | |||
=== Indole Derivatives === | |||
[[File:Indole_derivative.png|thumb|left|Structure of an indole derivative]] | |||
Indole derivatives are another class of compounds that have shown efficacy in inhibiting VEGFR-2. The indole moiety is often modified to enhance selectivity and potency. | |||
=== Pyrimidine Derivatives === | |||
[[File:Pyrimidine_derivative.png|thumb|right|Structure of a pyrimidine derivative]] | |||
Pyrimidine derivatives are characterized by a pyrimidine ring, which is essential for their interaction with the VEGFR-2 ATP binding site. | |||
== | === Pyridine Derivatives === | ||
[[File:Pyridine.png|thumb|left|Structure of a pyridine derivative]] | |||
Pyridine derivatives are also used as VEGFR-2 inhibitors. The pyridine ring contributes to the binding and inhibitory activity of these compounds. | |||
== | === Urea Derivatives === | ||
[[File:Harnstoff.svg|thumb|right|Structure of a urea derivative]] | |||
Urea derivatives are a class of VEGFR-2 inhibitors that utilize a urea linkage to enhance binding to the receptor. | |||
==Related Pages== | === Quinalone Derivatives === | ||
[[File:Quinalone_derivative.png|thumb|left|Structure of a quinalone derivative]] | |||
Quinalone derivatives are another group of compounds that have been developed as VEGFR-2 inhibitors, featuring a quinalone core structure. | |||
== Clinical Applications == | |||
VEGFR-2 inhibitors are primarily used in the treatment of various types of cancer, including [[renal cell carcinoma]], [[hepatocellular carcinoma]], and [[thyroid cancer]]. These inhibitors are often used in combination with other therapeutic agents to enhance their efficacy. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Angiogenesis]] | * [[Angiogenesis]] | ||
* [[Tyrosine kinase inhibitor]] | |||
* [[Cancer treatment]] | * [[Cancer treatment]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Vascular endothelial growth factor]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Antineoplastic drugs]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Tyrosine kinase inhibitors]] | ||
Revision as of 14:15, 21 February 2025
Overview
A VEGFR-2 inhibitor is a type of tyrosine kinase inhibitor that specifically targets the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2). VEGFR-2 is a key receptor involved in the process of angiogenesis, which is the formation of new blood vessels. Inhibiting VEGFR-2 can therefore be an effective strategy in the treatment of various cancers, as it can reduce the blood supply to tumors, inhibiting their growth and metastasis.
Mechanism of Action

VEGFR-2 inhibitors work by blocking the ATP binding site of the receptor, preventing its activation. This inhibition disrupts the downstream signaling pathways that promote endothelial cell proliferation and migration, which are essential for angiogenesis. By inhibiting these pathways, VEGFR-2 inhibitors can effectively reduce tumor vascularization and growth.
Chemical Classes
VEGFR-2 inhibitors belong to several chemical classes, each with distinct structural characteristics. Some of the notable classes include:
Quinazoline Derivatives

Quinazoline derivatives are a prominent class of VEGFR-2 inhibitors. These compounds typically feature a quinazoline core, which is crucial for their binding affinity to the receptor.
Indole Derivatives
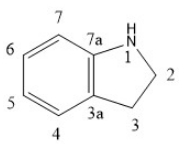
Indole derivatives are another class of compounds that have shown efficacy in inhibiting VEGFR-2. The indole moiety is often modified to enhance selectivity and potency.
Pyrimidine Derivatives
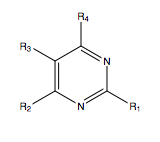
Pyrimidine derivatives are characterized by a pyrimidine ring, which is essential for their interaction with the VEGFR-2 ATP binding site.
Pyridine Derivatives

Pyridine derivatives are also used as VEGFR-2 inhibitors. The pyridine ring contributes to the binding and inhibitory activity of these compounds.
Urea Derivatives

Urea derivatives are a class of VEGFR-2 inhibitors that utilize a urea linkage to enhance binding to the receptor.
Quinalone Derivatives

Quinalone derivatives are another group of compounds that have been developed as VEGFR-2 inhibitors, featuring a quinalone core structure.
Clinical Applications
VEGFR-2 inhibitors are primarily used in the treatment of various types of cancer, including renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and thyroid cancer. These inhibitors are often used in combination with other therapeutic agents to enhance their efficacy.