Number: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
File:Khmer_Numerals_-_605_from_the_Sambor_inscriptions.jpg|Khmer numerals from the Sambor inscriptions | File:Khmer_Numerals_-_605_from_the_Sambor_inscriptions.jpg|Khmer numerals from the Sambor inscriptions | ||
File:Nat_num.svg|Number | File:Nat_num.svg|Number | ||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:NumberSetinC.svg|Number | |||
File:Khmer Numerals - 605 from the Sambor inscriptions.jpg|Number | |||
File:Nat num.svg|Number | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 01:08, 20 February 2025
Number
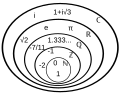
A Number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, and so forth. Numbers can be categorized into sets, called number systems, such as the natural numbers, integers, rational numbers, real numbers, and complex numbers.
History
The concept of number has been fundamental to the development of mathematics. The understanding of numbers has evolved over time from simple counting systems to the complex number systems we use today.
Types of Numbers
Natural Numbers
Natural numbers are the numbers used for counting (as in "there are six coins on the table") and ordering (as in "this is the third largest city in the country").
Integers
Integers are a larger group that contains the natural numbers and zero. They also include negative numbers.
Rational Numbers
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers.
Real Numbers
Real numbers include all the rational numbers, such as the integer ‑5 and the fraction 4/3, and all the irrational numbers, such as √2 (1.41421356..., the square root of two, an irrational algebraic number).
Complex Numbers
Complex numbers include all the numbers previously mentioned and also the imaginary numbers.