Aldol condensation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
[[Category:Organic reactions]] | [[Category:Organic reactions]] | ||
[[Category:Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions]] | [[Category:Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Condensationaldolique.png|Aldol_condensation | |||
File:Simple_aldol_reaction.svg|Aldol_condensation | |||
File:Base-catalysed_aldol_condensation.svg|Aldol_condensation | |||
File:Acid-catalysed_aldol_condensation.svg|Aldol_condensation | |||
File:Aldol_basisch_startAnimGif_1.gif|Aldol_condensation | |||
File:Aldol_sauer_startAnimGif_1.gif|Aldol_condensation | |||
File:Aldox_process.svg|Aldol_condensation | |||
File:Pentaerythritol_Synthesis.svg|Aldol_condensation | |||
File:Aldehyde_aldol_condensation_example.png|Aldol_condensation | |||
File:IsoprenetricarboxylicAcid2.png|Aldol_condensation | |||
File:RuCatalyzedCyclizationofTerminalAlkynalstoCycloalkenes.png|Aldol_condensation | |||
File:Menthone_Claisen-Schmidt.png|Aldol_condensation | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 12:03, 18 February 2025
A chemical reaction involving the formation of a _-hydroxy ketone or aldehyde
Aldol condensation is an important organic reaction in which an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form a _-hydroxy ketone or aldehyde, followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone. This reaction is a key step in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds in organic synthesis.
Mechanism
The aldol condensation can proceed via either a base-catalyzed or an acid-catalyzed mechanism.
Base-catalyzed mechanism
In the base-catalyzed aldol condensation, a base such as hydroxide or an alkoxide ion abstracts a proton from the _-carbon of a carbonyl compound, generating an enolate ion. This enolate ion then attacks the carbonyl carbon of another molecule, forming a _-hydroxy ketone or aldehyde. Subsequent dehydration leads to the formation of an _,_-unsaturated carbonyl compound.

Acid-catalyzed mechanism
In the acid-catalyzed aldol condensation, the carbonyl compound is protonated, making it more electrophilic. An enol form of the carbonyl compound then attacks the protonated carbonyl group, leading to the formation of a _-hydroxy ketone or aldehyde. Dehydration occurs to yield the _,_-unsaturated carbonyl compound.

Examples
A classic example of an aldol condensation is the reaction between acetaldehyde molecules to form crotonaldehyde.

Applications
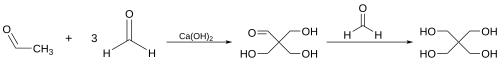
Aldol condensations are widely used in the synthesis of complex molecules, including natural products and pharmaceuticals. They are also employed in industrial processes, such as the production of pentaerythritol, a key component in the manufacture of alkyd resins.
Variations
Several variations of the aldol condensation exist, including the Henry reaction, the Robinson annulation, and the Claisen-Schmidt condensation. These variations expand the scope and utility of the aldol reaction in organic synthesis.
Related pages
Gallery
-
Illustration of aldol condensation
-
Simple aldol reaction
-
Base-catalyzed aldol reaction animation
-
Acid-catalyzed aldol reaction animation
-
Aldox process
-
Isoprene tricarboxylic acid synthesis
-
Ruthenium-catalyzed cyclization
-
Aldol_condensation
-
Aldol_condensation
-
Aldol_condensation
-
Aldol_condensation
-
Aldol_condensation
-
Aldol_condensation
-
Aldol_condensation
-
Aldol_condensation
-
Aldol_condensation
-
Aldol_condensation
-
Aldol_condensation
-
Aldol_condensation



