Agonal respiration: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
[[Category:Respiratory system]] | [[Category:Respiratory system]] | ||
[[Category:Medical emergencies]] | [[Category:Medical emergencies]] | ||
== Agonal_respiration == | |||
<gallery> | |||
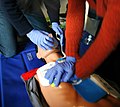
File:CPR_training-04.jpg|CPR training session | |||
File:Pyramid_(medulla_oblongata)_-_animation.gif|Animation of the medulla oblongata | |||
File:Afghanistan_-_cardiopulmonary_resuscitation.jpg|Cardiopulmonary resuscitation in Afghanistan | |||
File:Breathing_abnormalities.svg|Diagram of breathing abnormalities | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 04:27, 18 February 2025
Abnormal pattern of breathing characterized by gasping, labored breaths
Agonal respiration is an abnormal pattern of breathing characterized by gasping, labored breaths. It is often associated with severe medical conditions such as cardiac arrest or cerebral ischemia. Agonal respiration is considered a medical emergency and typically requires immediate intervention.
Characteristics
Agonal respiration is marked by irregular, gasping breaths that are often accompanied by strange vocalizations or moaning. These breaths are usually shallow and may occur at a slow rate. The pattern is often described as "gasping" because it resembles the reflexive gasps for air that occur when the body is deprived of oxygen.
Causes
Agonal respiration is most commonly associated with:
During these conditions, the brainstem, which controls basic life functions, may continue to send signals to the respiratory muscles, resulting in the characteristic gasping breaths.
Clinical Significance
Agonal respiration is a sign of severe distress and indicates that the body is not receiving adequate oxygen. It is often one of the last respiratory patterns observed before respiratory arrest.
Emergency Response
When agonal respiration is observed, it is crucial to initiate emergency medical services and begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) immediately. Agonal breaths are not effective in sustaining life, and CPR can help maintain circulation and oxygenation until advanced medical care is available.

Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of agonal respiration involves the brainstem's response to severe hypoxia or ischemia. The medulla oblongata, part of the brainstem, plays a critical role in controlling involuntary breathing. When the brain is deprived of oxygen, the medulla may still attempt to initiate breathing, resulting in the gasping pattern seen in agonal respiration.

Differential Diagnosis
Agonal respiration should be distinguished from other types of abnormal breathing patterns, such as:
Each of these patterns has distinct characteristics and underlying causes.
Related pages
Gallery
-
CPR being performed in Afghanistan.
-
Diagram of various breathing abnormalities.
Agonal_respiration
-
CPR training session
-
Animation of the medulla oblongata
-
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation in Afghanistan
-
Diagram of breathing abnormalities