Levonorgestrel butanoate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[Category:Drugs]] | [[Category:Drugs]] | ||
{{No image}} | {{No image}} | ||
== Levonorgestrel_butanoate == | |||
<gallery> | |||
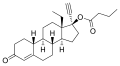
File:Levonorgestrel_butanoate.svg|Levonorgestrel butanoate chemical structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 21:15, 23 February 2025
Levonorgestrel Butanoate is a progestin medication which is used in birth control and hormone therapy. It is a long-acting, injectable form of levonorgestrel, a hormone that prevents ovulation and causes changes in the cervical mucus and uterine lining, making it harder for sperm to reach the uterus and harder for a fertilized egg to attach to the uterus.
Pharmacology
Levonorgestrel butanoate is a progestogen, or an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. It has weak androgenic and glucocorticoid activity and no other important hormonal activity.
Medical Uses
Levonorgestrel butanoate is used in birth control to prevent pregnancy. It is also used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and in the treatment of gynecological disorders.
Side Effects
Common side effects of levonorgestrel butanoate include menstrual irregularities, headache, nausea, breast tenderness, and mood changes. Rare but serious side effects include blood clots, liver disease, and breast cancer.
History
Levonorgestrel butanoate was developed in the 1970s and 1980s and has been used in Europe and Asia for many years. It is not currently available in the United States or Canada.
See Also
Levonorgestrel_butanoate
-
Levonorgestrel butanoate chemical structure