Dinitolmide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
{{No image}} | {{No image}} | ||
{{No image}} | {{No image}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Zoalene.png|Zoalene | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 00:02, 25 February 2025
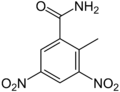
Dinitolmide (also known as Zoalene) is a chemical compound used as a coccidiostat. It is a feed additive used in poultry production to prevent coccidiosis, a parasitic disease of the intestinal tract caused by the ingestion of infected fecal matter.
Etymology
The name "Dinitolmide" is derived from its chemical structure, which contains two nitro groups (di-nitro) and a toluene group (tolmide).
History
Dinitolmide was first introduced in the 1950s as a coccidiostat for poultry. It was marketed under the trade name Zoalene and was the first product of its kind to be used in the poultry industry.
Use
Dinitolmide is used as a feed additive in the poultry industry to prevent coccidiosis. It is typically mixed with feed and given to poultry in a controlled dosage. The compound works by inhibiting the growth and reproduction of the coccidia parasites, thus preventing the disease.
Side Effects
While Dinitolmide is generally considered safe for use in poultry, it can cause some side effects. These may include reduced feed intake, weight loss, and in some cases, mortality. It is therefore important to use the compound in a controlled manner and under the supervision of a veterinarian.
Related Compounds
Dinitolmide is part of a class of compounds known as coccidiostats. Other compounds in this class include Amprolium, Decoquinate, and Halofuginone. These compounds work in a similar manner to Dinitolmide, by inhibiting the growth and reproduction of coccidia parasites.
See Also
References
<references />