Trapezoid bone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[Category:Carpal bones]] | [[Category:Carpal bones]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Trapezoid_bone_(left_hand)_01_palmar_view.png|Trapezoid bone | |||
File:Gray226.png|Trapezoid bone | |||
File:Trapezoid_bone_(left_hand)_-_animation01.gif|Trapezoid bone | |||
File:Trapezoid_bone_(left_hand)_-_animation02.gif|Trapezoid bone | |||
File:Trapezoid_bone.jpg|Trapezoid bone | |||
File:RightHumanPosteriorDistalRadiusUlnaCarpals_-_Trapezoid_bone.png|Trapezoid bone | |||
File:Gray220_-_Trapezoid_bone.png|Trapezoid bone | |||
File:Gray219_-_Trapezoid_bone.png|Trapezoid bone | |||
File:Gray422_-_Trapezoid_bone.png|Trapezoid bone | |||
File:Ospoignet_-_Trapezoid_bone.png|Trapezoid bone | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 11:49, 18 February 2025
Bone of the human wrist
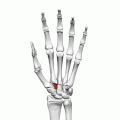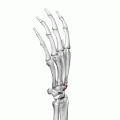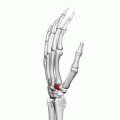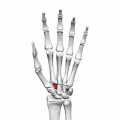
The trapezoid bone, also known as the lesser multangular bone, is one of the eight carpal bones of the wrist. It is located in the distal row of carpal bones and is the smallest bone in this row. The trapezoid bone is situated between the trapezium bone and the capitate bone, and it articulates with the second metacarpal bone.
Structure
The trapezoid bone is wedge-shaped and has four articular surfaces. The superior surface is concave and articulates with the scaphoid bone. The inferior surface is convex and articulates with the base of the second metacarpal bone. The lateral surface articulates with the trapezium bone, and the medial surface articulates with the capitate bone.
The dorsal and palmar surfaces of the trapezoid bone are rough for the attachment of ligaments. The bone is surrounded by a fibrous capsule that is part of the wrist joint complex.
Function
The trapezoid bone plays a crucial role in the stability and movement of the wrist. It helps to form the carpal arch, which is important for the passage of tendons and the median nerve through the carpal tunnel. The articulation with the second metacarpal bone allows for the movement of the index finger.
Clinical significance
Injuries to the trapezoid bone are rare but can occur due to trauma or repetitive stress. Fractures of the trapezoid bone can lead to pain and limited movement in the wrist. Diagnosis is typically made through X-ray or MRI imaging.
Gallery
-
Palmar view of the trapezoid bone in the left hand
-
Illustration showing the position of the trapezoid bone
-
Animation of the trapezoid bone in the left hand
-
Another animation of the trapezoid bone in the left hand
-
Image of the trapezoid bone
-
Posterior view of the trapezoid bone
-
Diagram showing the trapezoid bone
-
Lateral view of the trapezoid bone
-
Detailed illustration of the trapezoid bone
-
Anatomical drawing of the trapezoid bone
Related pages
References
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
-
Trapezoid bone
-
Trapezoid bone
-
Trapezoid bone
-
Trapezoid bone
-
Trapezoid bone
-
Trapezoid bone
-
Trapezoid bone
-
Trapezoid bone
-
Trapezoid bone
-
Trapezoid bone