Toothache: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
[[Category:Dental conditions]] | [[Category:Dental conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Oral pain]] | [[Category:Oral pain]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Address to the toothache.jpg|Toothache | |||
File:Pulpitis-gif.gif|Pulpitis | |||
File:Abscessed tooth periapical radiograph.jpg|Abscessed tooth periapical radiograph | |||
File:Open contact.jpg|Open contact | |||
File:Cracked tooth lateral periodontal abscess.jpg|Cracked tooth lateral periodontal abscess | |||
File:Ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis.jpg|Ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis | |||
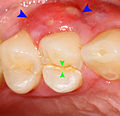
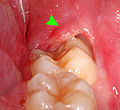
File:38 pericoronitis with pus.jpg|Pericoronitis with pus | |||
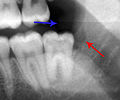
File:38 pericornitis xray.jpg|Pericoronitis x-ray | |||
File:Cracked tooth.png|Cracked tooth | |||
File:Angina pectoris.png|Angina pectoris | |||
File:Cross sections of teeth labels.png|Cross sections of teeth | |||
File:Innervation of the dentition.png|Innervation of the dentition | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:35, 20 February 2025
Pain in or around a tooth
| Toothache | |
|---|---|
| Address to the toothache.jpg | |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Pain in or around a tooth |
| Complications | Infection, abscess |
| Onset | N/A |
| Duration | N/A |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Dental caries, pulpitis, abscess |
| Risks | N/A |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, radiographs |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Dental treatment, pain management |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | N/A |
| Deaths | N/A |
A toothache is pain in or around a tooth. It can be caused by a variety of dental issues, including dental caries, pulpitis, and dental abscess. Toothaches can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and can significantly affect a person's quality of life.
Causes[edit]
Toothaches can be caused by several dental conditions:
- Dental caries: Also known as cavities, these are caused by the breakdown of tooth enamel due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth.
- Pulpitis: Inflammation of the dental pulp, which can be reversible or irreversible. Reversible pulpitis is mild and can be treated by removing the irritant, while irreversible pulpitis requires more extensive treatment such as a root canal.
- Dental abscess: A collection of pus that can form in different regions of the tooth due to bacterial infection. It can cause severe pain and swelling.
- Gingivitis and Periodontitis: Inflammation of the gums and supporting structures of the teeth can also lead to toothache.
- Tooth fracture: A cracked or broken tooth can expose the sensitive inner layers of the tooth, leading to pain.
Symptoms[edit]
The primary symptom of a toothache is pain in or around a tooth. The pain can be sharp, throbbing, or constant. In some cases, pain occurs only when pressure is applied to the tooth. Other symptoms that may accompany a toothache include:
- Swelling around the tooth
- Fever or headache
- Foul-tasting drainage from the infected tooth
- Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of a toothache involves a clinical examination by a dentist. The dentist will:
- Take a detailed history of the pain and any other symptoms
- Perform a physical examination of the mouth, teeth, and gums
- Use diagnostic tools such as dental radiographs (X-rays) to identify the underlying cause of the pain
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for a toothache depends on the underlying cause:
- Dental caries: Treatment may involve filling the cavity or, in severe cases, performing a root canal.
- Pulpitis: Reversible pulpitis can be treated by removing the irritant and restoring the tooth. Irreversible pulpitis may require a root canal or extraction.
- Dental abscess: Treatment involves draining the abscess and eliminating the infection, often through a root canal or extraction.
- Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain until dental treatment is received.
Prevention[edit]
Preventing toothaches involves maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups. Key preventive measures include:
- Brushing teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
- Flossing daily to remove plaque between teeth
- Limiting sugary foods and drinks
- Regular dental visits for cleanings and examinations
Also see[edit]
-
Toothache
-
Pulpitis
-
Abscessed tooth periapical radiograph
-
Open contact
-
Cracked tooth lateral periodontal abscess
-
Ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis
-
Pericoronitis with pus
-
Pericoronitis x-ray
-
Cracked tooth
-
Angina pectoris
-
Cross sections of teeth
-
Innervation of the dentition