Parliament of Australia: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Australian House of Representatives chart.svg|thumb]] [[File:2022 Election Australian Senate - Composition of Members.svg|thumb]] [[File:Opening of the first parliament.jpg|thumb]] [[File:Parliament House Melbourne 2010.jpg|thumb]] {{Infobox legislature | ||
{{Infobox legislature | |||
| name = Parliament of Australia | | name = Parliament of Australia | ||
| native_name = | | native_name = | ||
| native_name_lang = | |||
| transcription_name = | |||
| legislature = | | legislature = | ||
| coa_pic = Coat of Arms of Australia.svg | | coa_pic = Coat of Arms of Australia.svg | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| coa_alt = | | coa_alt = | ||
| house_type = Bicameral | | house_type = Bicameral | ||
| body = | |||
| houses = [[Senate (Australia)|Senate]] | | houses = [[Senate (Australia)|Senate]] | ||
[[House of Representatives (Australia)|House of Representatives]] | [[House of Representatives (Australia)|House of Representatives]] | ||
| leader1_type = | | leader1_type = Monarch | ||
| leader1 = [[Charles III]] | | leader1 = [[Charles III]] | ||
| leader2_type = | | leader2_type = Governor-General | ||
| leader2 = [[David Hurley]] | | leader2 = [[David Hurley]] | ||
| leader3_type = | | leader3_type = President of the Senate | ||
| leader3 = [[Sue Lines]] | |||
| leader4_type = Speaker of the House of Representatives | |||
| | | leader4 = [[Milton Dick]] | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| structure1 = | | structure1 = | ||
| structure1_res = | |||
| structure2 = | | structure2 = | ||
| structure2_res = | |||
| voting_system1 = [[Single transferable vote]] | | voting_system1 = [[Single transferable vote]] | ||
| voting_system2 = [[Instant-runoff voting]] | | voting_system2 = [[Instant-runoff voting]] | ||
| last_election1 = | | last_election1 = 21 May 2022 | ||
| last_election2 = | | last_election2 = 21 May 2022 | ||
| session_room = | | session_room = Parliament House Canberra.jpg | ||
| session_res = 250px | | session_res = 250px | ||
| session_alt = | | session_alt = | ||
| meeting_place = [[Parliament House, | | meeting_place = [[Parliament House, Canberra]] | ||
| website = | | website = [https://www.aph.gov.au/ www.aph.gov.au] | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Parliament of Australia''' is the | The '''Parliament of Australia''' is the federal legislature of the Commonwealth of Australia, consisting of three elements: the [[Monarch]], the [[Senate (Australia)|Senate]], and the [[House of Representatives (Australia)|House of Representatives]]. It is a bicameral legislature, meaning it has two houses, and it is based on the Westminster system of parliamentary government. | ||
== Structure == | ==Structure and Function== | ||
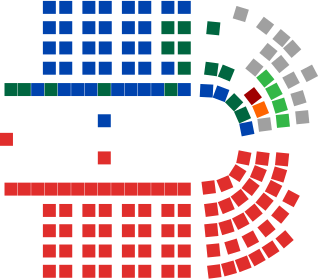
The Parliament of Australia is composed of the | The Parliament of Australia is composed of two houses: the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Senate is often referred to as the "upper house," while the House of Representatives is known as the "lower house." | ||
=== | ===The Senate=== | ||
The | The Senate consists of 76 senators. Each of the six states of Australia is represented by 12 senators, regardless of population, while the two territories, the [[Australian Capital Territory]] and the [[Northern Territory]], are each represented by two senators. Senators are elected using a proportional representation voting system known as the [[Single transferable vote]]. | ||
The Senate's primary role is to represent the states and territories of Australia, review legislation proposed by the House of Representatives, and act as a house of review. It has the power to reject or amend bills, except for money bills, which it cannot initiate. | |||
The | |||
=== House of Representatives === | ===The House of Representatives=== | ||
The | The House of Representatives consists of 151 members, each representing an electoral division. Members are elected using the [[Instant-runoff voting]] system, also known as preferential voting. The number of members from each state and territory is based on population, with each member representing approximately the same number of voters. | ||
== | The House of Representatives is the house where government is formed. The political party or coalition with the majority of seats in the House forms the government, and its leader becomes the [[Prime Minister of Australia|Prime Minister]]. The House is responsible for proposing and debating legislation, particularly money bills, which must originate in the House. | ||
The | |||
==Legislative Process== | |||
The legislative process in the Parliament of Australia involves several stages: | |||
1. '''First Reading''': A bill is introduced in either house (except money bills, which must start in the House of Representatives) and is read for the first time. | |||
2. '''Second Reading''': The general principles of the bill are debated, and a vote is taken. | |||
3. '''Committee Stage''': The bill is examined in detail by a committee of the whole house or a select committee. | |||
4. '''Third Reading''': The final version of the bill is debated and voted on. | |||
5. '''Senate Consideration''': If the bill passes one house, it is sent to the other house for consideration. | |||
6. '''Royal Assent''': Once both houses agree on the bill, it is sent to the Governor-General for royal assent and becomes law. | |||
==Powers and Responsibilities== | |||
The Parliament of Australia has several key powers and responsibilities, including: | |||
* Making and amending laws | * Making and amending laws | ||
* | * Approving the budget and government expenditure | ||
* | * Scrutinizing the actions of the government | ||
* | * Representing the Australian people | ||
==History== | |||
The Parliament of Australia was established by the [[Constitution of Australia]], which came into effect on 1 January 1901. The first meeting of the Parliament was held in Melbourne on 9 May 1901. In 1927, the Parliament moved to [[Canberra]], the capital city of Australia, where it has remained since. | |||
== | ==Also see== | ||
* [[Government of Australia]] | * [[Government of Australia]] | ||
* [[Prime Minister of Australia]] | * [[Prime Minister of Australia]] | ||
* [[Governor-General of Australia]] | * [[Governor-General of Australia]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Constitution of Australia]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Australian electoral system]] | ||
{{Australian politics}} | |||
[[Category:Parliament of Australia]] | [[Category:Parliament of Australia]] | ||
[[Category:Australian government]] | [[Category:Australian government]] | ||
[[Category:Legislatures]] | [[Category:Legislatures]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:25, 9 December 2024



The Parliament of Australia is the federal legislature of the Commonwealth of Australia, consisting of three elements: the Monarch, the Senate, and the House of Representatives. It is a bicameral legislature, meaning it has two houses, and it is based on the Westminster system of parliamentary government.
Structure and Function[edit]
The Parliament of Australia is composed of two houses: the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Senate is often referred to as the "upper house," while the House of Representatives is known as the "lower house."
The Senate[edit]
The Senate consists of 76 senators. Each of the six states of Australia is represented by 12 senators, regardless of population, while the two territories, the Australian Capital Territory and the Northern Territory, are each represented by two senators. Senators are elected using a proportional representation voting system known as the Single transferable vote.
The Senate's primary role is to represent the states and territories of Australia, review legislation proposed by the House of Representatives, and act as a house of review. It has the power to reject or amend bills, except for money bills, which it cannot initiate.
The House of Representatives[edit]
The House of Representatives consists of 151 members, each representing an electoral division. Members are elected using the Instant-runoff voting system, also known as preferential voting. The number of members from each state and territory is based on population, with each member representing approximately the same number of voters.
The House of Representatives is the house where government is formed. The political party or coalition with the majority of seats in the House forms the government, and its leader becomes the Prime Minister. The House is responsible for proposing and debating legislation, particularly money bills, which must originate in the House.
Legislative Process[edit]
The legislative process in the Parliament of Australia involves several stages:
1. First Reading: A bill is introduced in either house (except money bills, which must start in the House of Representatives) and is read for the first time. 2. Second Reading: The general principles of the bill are debated, and a vote is taken. 3. Committee Stage: The bill is examined in detail by a committee of the whole house or a select committee. 4. Third Reading: The final version of the bill is debated and voted on. 5. Senate Consideration: If the bill passes one house, it is sent to the other house for consideration. 6. Royal Assent: Once both houses agree on the bill, it is sent to the Governor-General for royal assent and becomes law.
Powers and Responsibilities[edit]
The Parliament of Australia has several key powers and responsibilities, including:
- Making and amending laws
- Approving the budget and government expenditure
- Scrutinizing the actions of the government
- Representing the Australian people
History[edit]
The Parliament of Australia was established by the Constitution of Australia, which came into effect on 1 January 1901. The first meeting of the Parliament was held in Melbourne on 9 May 1901. In 1927, the Parliament moved to Canberra, the capital city of Australia, where it has remained since.
Also see[edit]
- Government of Australia
- Prime Minister of Australia
- Governor-General of Australia
- Constitution of Australia
- Australian electoral system
| Politics of Australia | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|