Ciliopathy: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Eukaryotic_cilium_diagram_en.svg|thumb | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Ciliopathy | |||
| image = [[File:Eukaryotic_cilium_diagram_en.svg|250px]] | |||
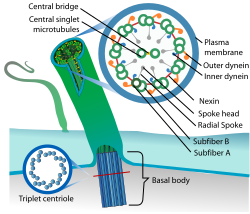
| caption = Diagram of a eukaryotic cilium | |||
| field = [[Medical genetics]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Kidney disease]], [[retinal degeneration]], [[liver fibrosis]], [[cognitive impairment]] | |||
| complications = [[Organ failure]], [[blindness]], [[infertility]] | |||
| onset = Varies by specific condition | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| causes = Genetic mutations affecting [[cilia]] | |||
| risks = Family history of ciliopathies | |||
| diagnosis = [[Genetic testing]], [[imaging studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Polycystic kidney disease]], [[Bardet-Biedl syndrome]], [[Alström syndrome]] | |||
| treatment = Symptomatic management, [[organ transplantation]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies depending on specific condition and severity | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Eukaryotic_cilium_diagram_en.svg|left|thumb]] '''Ciliopathy''' is a group of genetic disorders caused by the dysfunction of [[cilia]], which are hair-like structures present on the surface of most eukaryotic cells. These disorders can affect multiple organ systems and lead to a wide range of clinical manifestations. | |||
==Structure and Function of Cilia== | ==Structure and Function of Cilia== | ||
[[Cilia]] are classified into two main types: [[motile cilia]] and [[primary cilia]]. Motile cilia are involved in movement, such as the clearing of mucus in the respiratory tract, while primary cilia function as sensory organelles, playing a crucial role in signal transduction pathways. | [[Cilia]] are classified into two main types: [[motile cilia]] and [[primary cilia]]. Motile cilia are involved in movement, such as the clearing of mucus in the respiratory tract, while primary cilia function as sensory organelles, playing a crucial role in signal transduction pathways. | ||
==Genetics== | ==Genetics== | ||
Ciliopathies are typically inherited in an [[autosomal recessive]] manner, although some can be [[autosomal dominant]]. Mutations in genes encoding proteins that are part of the ciliary structure or its associated machinery can lead to ciliopathies. Some of the genes commonly associated with ciliopathies include [[PKD1]], [[PKD2]], and [[IFT88]]. | Ciliopathies are typically inherited in an [[autosomal recessive]] manner, although some can be [[autosomal dominant]]. Mutations in genes encoding proteins that are part of the ciliary structure or its associated machinery can lead to ciliopathies. Some of the genes commonly associated with ciliopathies include [[PKD1]], [[PKD2]], and [[IFT88]]. | ||
==Clinical Manifestations== | ==Clinical Manifestations== | ||
Ciliopathies can present with a wide range of symptoms, depending on the organs affected. Common clinical features include: | Ciliopathies can present with a wide range of symptoms, depending on the organs affected. Common clinical features include: | ||
| Line 15: | Line 30: | ||
* [[Skeletal abnormalities]] | * [[Skeletal abnormalities]] | ||
* [[Intellectual disability]] | * [[Intellectual disability]] | ||
==Types of Ciliopathies== | ==Types of Ciliopathies== | ||
Several specific disorders fall under the umbrella of ciliopathies, including: | Several specific disorders fall under the umbrella of ciliopathies, including: | ||
| Line 24: | Line 38: | ||
* [[Nephronophthisis]] | * [[Nephronophthisis]] | ||
* [[Alström syndrome]] | * [[Alström syndrome]] | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of ciliopathies often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and genetic testing. [[Ultrasound]] and [[MRI]] can be used to identify structural abnormalities in organs such as the kidneys and liver. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in cilia-related genes. | Diagnosis of ciliopathies often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and genetic testing. [[Ultrasound]] and [[MRI]] can be used to identify structural abnormalities in organs such as the kidneys and liver. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in cilia-related genes. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
There is currently no cure for ciliopathies, and treatment is primarily supportive and symptomatic. Management strategies may include: | There is currently no cure for ciliopathies, and treatment is primarily supportive and symptomatic. Management strategies may include: | ||
| Line 33: | Line 45: | ||
* [[Physical therapy]] and [[occupational therapy]] for motor and developmental delays | * [[Physical therapy]] and [[occupational therapy]] for motor and developmental delays | ||
* [[Surgical interventions]] for structural abnormalities | * [[Surgical interventions]] for structural abnormalities | ||
==Research== | ==Research== | ||
Ongoing research aims to better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying ciliopathies and to develop targeted therapies. Advances in [[gene therapy]] and [[stem cell research]] hold promise for future treatment options. | Ongoing research aims to better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying ciliopathies and to develop targeted therapies. Advances in [[gene therapy]] and [[stem cell research]] hold promise for future treatment options. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Cilia]] | * [[Cilia]] | ||
| Line 43: | Line 53: | ||
* [[Bardet-Biedl syndrome]] | * [[Bardet-Biedl syndrome]] | ||
* [[Joubert syndrome]] | * [[Joubert syndrome]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
{{Commons category|Ciliopathy}} | {{Commons category|Ciliopathy}} | ||
[[Category:Genetic disorders]] | [[Category:Genetic disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | [[Category:Rare diseases]] | ||
| Line 55: | Line 62: | ||
[[Category:Neurology]] | [[Category:Neurology]] | ||
[[Category:Ophthalmology]] | [[Category:Ophthalmology]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 02:05, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Ciliopathy | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Kidney disease, retinal degeneration, liver fibrosis, cognitive impairment |
| Complications | Organ failure, blindness, infertility |
| Onset | Varies by specific condition |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutations affecting cilia |
| Risks | Family history of ciliopathies |
| Diagnosis | Genetic testing, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Polycystic kidney disease, Bardet-Biedl syndrome, Alström syndrome |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Symptomatic management, organ transplantation |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on specific condition and severity |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

Ciliopathy is a group of genetic disorders caused by the dysfunction of cilia, which are hair-like structures present on the surface of most eukaryotic cells. These disorders can affect multiple organ systems and lead to a wide range of clinical manifestations.
Structure and Function of Cilia[edit]
Cilia are classified into two main types: motile cilia and primary cilia. Motile cilia are involved in movement, such as the clearing of mucus in the respiratory tract, while primary cilia function as sensory organelles, playing a crucial role in signal transduction pathways.
Genetics[edit]
Ciliopathies are typically inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, although some can be autosomal dominant. Mutations in genes encoding proteins that are part of the ciliary structure or its associated machinery can lead to ciliopathies. Some of the genes commonly associated with ciliopathies include PKD1, PKD2, and IFT88.
Clinical Manifestations[edit]
Ciliopathies can present with a wide range of symptoms, depending on the organs affected. Common clinical features include:
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Retinal degeneration
- Liver fibrosis
- Obesity
- Skeletal abnormalities
- Intellectual disability
Types of Ciliopathies[edit]
Several specific disorders fall under the umbrella of ciliopathies, including:
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Bardet-Biedl syndrome
- Joubert syndrome
- Meckel-Gruber syndrome
- Nephronophthisis
- Alström syndrome
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of ciliopathies often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and genetic testing. Ultrasound and MRI can be used to identify structural abnormalities in organs such as the kidneys and liver. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in cilia-related genes.
Treatment[edit]
There is currently no cure for ciliopathies, and treatment is primarily supportive and symptomatic. Management strategies may include:
- Dialysis or kidney transplantation for renal failure
- Physical therapy and occupational therapy for motor and developmental delays
- Surgical interventions for structural abnormalities
Research[edit]
Ongoing research aims to better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying ciliopathies and to develop targeted therapies. Advances in gene therapy and stem cell research hold promise for future treatment options.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
External Links[edit]
