Monte Carlo method: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
{{Mathematics-stub}} | {{Mathematics-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Approximation_d'une_distribution_normale.gif|Approximation of a normal distribution | |||
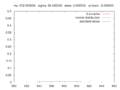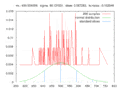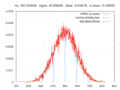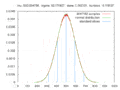
File:Pi_monte_carlo_all.gif|Monte Carlo method for approximating Pi | |||
File:Monte-carlo2.gif|Monte Carlo simulation | |||
File:Monte-Carlo_method_(errors).png|Monte Carlo method (errors) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:31, 18 February 2025
Monte Carlo methods are a broad class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results. The underlying concept is to use randomness to solve problems that might be deterministic in principle. They are used in a wide range of applications from physics, engineering, finance, statistics, to mathematics, allowing for the modeling of complex systems and the computation of difficult integrals.
Overview[edit]
Monte Carlo methods are particularly useful in scenarios where analytical solutions are impractical or impossible to obtain. They work by simulating random variables that have the same statistical properties as the system under study. By analyzing the outcomes of these simulations, researchers can approximate solutions to problems such as calculating π, solving physical equations, or pricing complex financial instruments.
History[edit]
The development of Monte Carlo methods can be traced back to the 1940s, with notable contributions from scientists such as Stanislaw Ulam, John von Neumann, and Enrico Fermi. The name "Monte Carlo" was coined by Ulam and von Neumann, inspired by the Monte Carlo Casino in Monaco, reflecting the stochastic (or random) nature of the methods, akin to gambling.
Applications[edit]
Physics[edit]
In physics, Monte Carlo methods are used in statistical physics, quantum mechanics, and radiation transport problems. They are crucial in the study of systems with a large number of coupled degrees of freedom.
Finance[edit]
In finance, these methods are applied to the valuation of options and other derivatives, as well as in risk management. Monte Carlo simulations can model the various sources of uncertainty affecting the value of financial instruments and the financial market as a whole.
Engineering[edit]
Engineering applications include the analysis of system reliability and safety, as well as in the design and optimization of complex systems.
Biology[edit]
In biology, Monte Carlo methods are used in bioinformatics for sequence alignment, and in systems biology for the simulation of biological processes.
Mathematics[edit]
In mathematics, these methods are employed to solve complex integrals and in numerical analysis.
Algorithm[edit]
The basic algorithm of a Monte Carlo simulation involves: 1. Defining a domain of possible inputs. 2. Generating inputs randomly from a probability distribution over the domain. 3. Performing a deterministic computation on the inputs. 4. Aggregating the results.
Advantages and Disadvantages[edit]
The main advantage of Monte Carlo methods is their ability to handle complex problems across various fields. However, they can be computationally intensive and require a significant number of simulations to achieve accurate results, especially for systems with a high degree of complexity.
See Also[edit]

This article is a mathematics-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Approximation of a normal distribution
-
Monte Carlo method for approximating Pi
-
Monte Carlo simulation
-
Monte Carlo method (errors)