Phenylene group: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
[[Category:Organic chemistry]] | [[Category:Organic chemistry]] | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
==Phenylene group== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:P-phenylene-group-2D-skeletal.png|P-phenylene group 2D skeletal | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:00, 3 March 2025
Phenylene is a hydrocarbon group derived from benzene by the removal of a hydrogen atom, which results in the formula C6H4. It is a fundamental unit in organic chemistry and plays a crucial role in the structure of many organic compounds, including polymers, dyes, and pharmaceuticals. The phenylene group is known for its stability and aromaticity, which contribute to the properties of compounds containing this group.
Structure and Properties[edit]
The phenylene group consists of a six-carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds, a configuration that is characteristic of aromatic compounds. This structure is responsible for the group's notable stability and its ability to participate in a wide range of chemical reactions. The electrons in the phenylene group are delocalized over the ring, contributing to its aromaticity and chemical resilience.
Types of Phenylene Groups[edit]
There are three isomeric forms of the phenylene group, distinguished by the positioning of the two remaining bonds that are not part of the aromatic ring. These isomers are:
- Ortho-phenylene (1,2-phenylene)
- Meta-phenylene (1,3-phenylene)
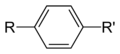
- Para-phenylene (1,4-phenylene)
Each of these isomers has unique properties and is suited to different chemical applications.
Applications[edit]
Phenylene groups are integral to a wide variety of compounds with important industrial and pharmaceutical applications. Some of the key areas where phenylene groups are utilized include:
- Polymers: Phenylene groups are building blocks for high-performance polymers such as Kevlar and Nomex, which are known for their strength and thermal stability.
- Dyes and Pigments: Many dyes and pigments contain phenylene groups, which contribute to their stability and color properties.
- Pharmaceuticals: Several drugs feature phenylene groups in their molecular structures, where they can influence the biological activity of the compound.
Synthesis[edit]
The synthesis of compounds containing phenylene groups can be achieved through various methods, including the direct aromatic substitution of benzene derivatives. The choice of synthesis method depends on the desired phenylene isomer and the specific application of the compound being produced.
Environmental and Health Considerations[edit]
While compounds containing phenylene groups are crucial in many applications, it is important to consider their environmental and health impacts. Some compounds, particularly certain polymers and dyes, can pose risks if not handled and disposed of properly.
Conclusion[edit]
The phenylene group is a versatile and important component in the field of organic chemistry, with a wide range of applications in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and beyond. Its stability, aromaticity, and the ability to form various isomers make it a valuable building block in the synthesis of complex organic compounds.
Phenylene group[edit]
-
P-phenylene group 2D skeletal