Oxazines: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Oxazines.svg|Oxazines | |||
File:DioxazineFrChloranil.png|Dioxazine from Chloranil | |||
File:Benzoxazine_resins.jpg|Benzoxazine Resins | |||
File:Morpholine-flat-2D-skeletal.png|Morpholine Structure | |||
File:10H-phenoxazine_200.svg|10H-Phenoxazine | |||
File:C.I._Pigment_Violet_23.svg|C.I. Pigment Violet 23 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:33, 18 February 2025
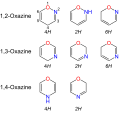
Oxazines are a group of organic compounds in the heterocyclic class, characterized by a six-membered ring structure that includes one oxygen atom and one nitrogen atom. The general formula for oxazines is C_4H_4NO. These compounds are significant in various chemical reactions and have applications in the synthesis of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. Oxazines can exist in several isomeric forms, depending on the positions of the oxygen and nitrogen atoms within the ring. The most common isomers are 1,2-oxazine, 1,3-oxazine, and 1,4-oxazine, each having distinct chemical properties and applications.
Structure and Isomerism[edit]
Oxazines are part of a larger family of heterocyclic compounds. The structure of an oxazine ring can be altered by the position of its heteroatoms (oxygen and nitrogen), leading to different isomers:
- 1,2-Oxazine - Also known as isooxazine, features the oxygen and nitrogen atoms adjacent to each other.
- 1,3-Oxazine - The oxygen and nitrogen atoms are separated by one carbon atom.
- 1,4-Oxazine - The oxygen and nitrogen atoms are separated by two carbon atoms.
These structural variations significantly influence the chemical reactivity and applications of oxazines.
Synthesis[edit]
The synthesis of oxazines can be achieved through various methods, depending on the desired isomer. Common approaches include:
- The condensation of aldehydes or ketones with hydroxylamine and ethylene glycol or other diols in the presence of acid catalysts.
- Cyclodehydration of amino alcohols with carboxylic acids or their derivatives.
- Ring-closure reactions of dihydropyridines.
Each method offers pathways to different oxazine derivatives, highlighting the versatility of these compounds in synthetic chemistry.
Applications[edit]
Oxazines find applications in several fields, including:
- Dyes and Pigments: Certain oxazine compounds are used in the synthesis of textile dyes and pigments due to their vibrant colors and stability.
- Pharmaceuticals: Oxazine derivatives have been explored for their pharmacological properties, including antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities.
- Agrochemicals: Some oxazine compounds serve as intermediates in the synthesis of pesticides and herbicides.
Pharmacology[edit]
The pharmacological interest in oxazines is due to their potential therapeutic properties. Research has identified oxazine derivatives with various biological activities, which could lead to the development of new drugs. However, the medicinal chemistry of oxazines is complex, and their mechanisms of action often require further investigation.
Safety and Toxicology[edit]
The safety profile of oxazine compounds varies widely among different derivatives. While some may be benign, others can exhibit toxicity, necessitating careful handling and assessment in their use, especially in pharmaceutical and agricultural applications.
-
Oxazines
-
Dioxazine from Chloranil
-
Benzoxazine Resins
-
Morpholine Structure
-
10H-Phenoxazine
-
C.I. Pigment Violet 23