Methyl bisulfate: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
== Methyl bisulfate gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Methyl hydrogen sulfate.png|Methyl hydrogen sulfate | |||
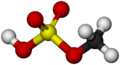
File:Methyl bisulfate-Molecule-3D-balls-by-AHRLS 2011.png|Methyl bisulfate Molecule 3D balls | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:48, 3 March 2025
Methyl bisulfate, also known as methyl hydrogen sulfate, is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CH3HSO4. It is an organic ester formed from methanol and sulfuric acid. This compound is a colorless, oily liquid that is soluble in water and organic solvents. Methyl bisulfate is used in various chemical synthesis processes, particularly in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries, due to its role as a methylating agent.
Properties[edit]
Methyl bisulfate is characterized by its strong acidic nature, which is attributed to the presence of the sulfate group. It has a boiling point of approximately 185°C (365°F) and a molecular weight of 112.11 g/mol. The compound's solubility in water and organic solvents like ethanol and acetone makes it a versatile reagent in organic synthesis.
Synthesis[edit]
The synthesis of methyl bisulfate typically involves the reaction of methanol with sulfuric acid. This process requires careful control of reaction conditions to prevent the formation of dimethyl sulfate, a potent and dangerous methylating agent.
Applications[edit]
Methyl bisulfate is primarily used as a methylating agent in organic synthesis. Its applications include:
- Synthesis of pharmaceuticals: It is used in the production of various drugs, acting as an intermediate in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- Agrochemical production: Methyl bisulfate serves as a precursor in the synthesis of pesticides and herbicides.
- Chemical research: In academic and industrial research laboratories, it is employed in methylation reactions to introduce methyl groups into organic molecules.
Safety[edit]
Handling methyl bisulfate requires caution due to its corrosive nature and potential health hazards. It can cause severe skin burns and eye damage upon contact. Inhalation or ingestion of methyl bisulfate can lead to serious respiratory and digestive tract issues. Appropriate safety measures, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and adequate ventilation, are essential when working with this compound.
Environmental Impact[edit]
The environmental impact of methyl bisulfate is associated with its toxicity to aquatic life. It should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations to minimize its release into the environment. Efforts to reduce its use and find safer alternatives are ongoing in the chemical industry.
Methyl bisulfate gallery[edit]
-
Methyl hydrogen sulfate
-
Methyl bisulfate Molecule 3D balls