Paradental cyst: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
[[Category:Cysts]] | [[Category:Cysts]] | ||
{{Oral pathology-stub}} | {{Oral pathology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
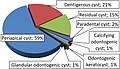
File:Relative_incidence_of_odontogenic_cysts.jpg|Relative incidence of odontogenic cysts | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:58, 16 February 2025
Paradental Cyst
A Paradental Cyst is a type of odontogenic cyst that is associated with the crown of an unerupted or partially erupted tooth. It is also known as a Buccal Bifurcation Cyst and is most commonly found in the lower jaw, specifically in the area of the mandibular molars.
Etiology[edit]
The exact cause of a paradental cyst is not known, but it is believed to be related to inflammation in the dental pulp, often due to an infection or trauma. The cyst forms in the dental follicle, the sac that surrounds the unerupted tooth.
Clinical Features[edit]
Paradental cysts are typically asymptomatic and are often discovered during routine dental radiographs. However, they can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty in opening the mouth if they become infected or if they grow large enough to press on nearby structures.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of a paradental cyst is usually made based on the clinical presentation and radiographic findings. The cyst appears as a radiolucent (dark) area on the radiograph, often associated with the root of a tooth. A definitive diagnosis can only be made through histopathological examination of the cyst after it has been surgically removed.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of choice for a paradental cyst is surgical removal, also known as cystectomy. This involves removing the entire cyst along with the associated tooth if it is unerupted or partially erupted. Antibiotics may also be prescribed if there is an associated infection.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for a paradental cyst is generally good, with a low recurrence rate after surgical removal. However, regular follow-up is necessary to monitor for any signs of recurrence.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
This article is a Oral pathology-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Relative incidence of odontogenic cysts