Volcanism: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
[[Category:Geology]] | [[Category:Geology]] | ||
{{Geology-stub}} | {{Geology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Magmatism_and_volcanism_EN.svg|Volcanism | |||
File:Volcanosed.svg|Volcanism | |||
File:Erupsi_Gunung_Sinabung.jpg|Eruption of Mount Sinabung | |||
File:Gryphons_at_the_central_crater_of_the_Dashgil_mud_volcano_in_Azerbaijan_(130).JPG|Mud volcano in Azerbaijan | |||
File:Kilauea_Fissure_8_cone_erupting_on_6-28-2018.jpg|Kilauea Fissure 8 eruption | |||
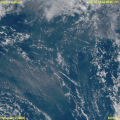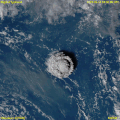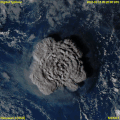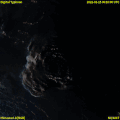
File:Tonga_Volcano_Eruption_2022-01-15_0320Z_to_0610Z_Himawari-8_visible.gif|Tonga Volcano Eruption 2022 | |||
File:PIA19059-SaturnMoon-Enceladus-OceanMethane-20150311.png|Enceladus Ocean Methane | |||
File:Olympus_Mons.jpeg|Olympus Mons | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 12:19, 18 February 2025
Volcanism is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a volcano. Volcanic phenomena include active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes, volcanic fields, and volcanic gases.
Types of Volcanism
Volcanism can be classified into two primary types: effusive and explosive.
Effusive Volcanism
Effusive volcanism involves the outpouring of lava onto the ground. This type of volcanism is characterized by the slow, steady outflow of magma, which often results in the formation of large, shield-like volcanoes. The Hawaiian Islands are a prime example of effusive volcanism.
Explosive Volcanism
Explosive volcanism is characterized by violent eruptions that can blast large amounts of rock, ash, and gas into the atmosphere. This type of volcanism often results in the formation of stratovolcanoes, such as Mount St. Helens in the United States.
Volcanic Features
Volcanic features include not only volcanoes themselves, but also a wide variety of other geological features, such as calderas, lava domes, lava tubes, and geysers.
Volcanoes
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
Calderas
A caldera is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber/reservoir in a volcanic eruption.
Lava Domes
A lava dome is a roughly circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano.
Lava Tubes
A lava tube is a natural conduit formed by flowing lava which moves beneath the hardened surface of a lava flow.
Geysers
A geyser is a spring characterized by intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by steam.
Effects of Volcanism
Volcanism has many effects, both positive and negative, on the environment and human societies. These include the creation of new land, the production of valuable minerals, the alteration of climate, and the potential for catastrophic eruptions.
See Also
-
Volcanism
-
Volcanism
-
Eruption of Mount Sinabung
-
Mud volcano in Azerbaijan
-
Kilauea Fissure 8 eruption
-
Tonga Volcano Eruption 2022
-
Enceladus Ocean Methane
-
Olympus Mons