Viscoelasticity: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{{Physics-stub}} | {{Physics-stub}} | ||
{{Materials-science-stub}} | {{Materials-science-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Non-Newtonian_fluid.svg|Viscoelasticity | |||
File:Elastic_v._viscoelastic_material.JPG|Elastic vs. Viscoelastic Material | |||
File:Comparison_three_four_element_models.svg|Comparison of Three and Four Element Models | |||
File:Maxwell_diagram.svg|Maxwell Diagram | |||
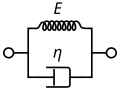
File:Kelvin_Voigt_diagram.svg|Kelvin-Voigt Diagram | |||
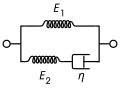
File:SLS.svg|Standard Linear Solid Model | |||
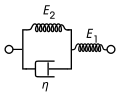
File:SLS2.svg|Standard Linear Solid Model 2 | |||
File:Jeffreys_rheological_model.svg|Jeffreys Rheological Model | |||
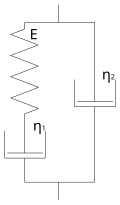
File:Burgers_model_2.svg|Burgers Model 2 | |||
File:Burgers_model.svg|Burgers Model | |||
File:Weichert.svg|Weichert Model | |||
File:Visco.jpg|Viscoelasticity | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 12:23, 18 February 2025
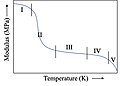
Viscoelasticity is a property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like honey, resist shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Elastic materials, like rubber, strain when stretched and quickly return to their original state once the stress is removed.
Overview
Viscoelasticity is a complex property of a material represented by the tensor of viscosity for viscous materials and the tensor of elasticity for elastic materials. These tensors are combined into a single tensor in viscoelastic materials.
Mathematical Description
The mathematical models used to describe viscoelastic materials are the Maxwell model, the Kelvin-Voigt model, and the Standard Linear Solid Model. These models use differential equations to describe the material's response to stress and strain.
Applications
Viscoelasticity has a wide range of applications in various fields such as biomechanics, polymer physics, and rheology. In biomechanics, it is used to model the behavior of human tissue in response to stress. In polymer physics, it is used to describe the behavior of polymers in molten or solid state. In rheology, it is used to describe the flow of fluids that have a complex microstructure.
See Also
This article is a Materials science-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Viscoelasticity
-
Elastic vs. Viscoelastic Material
-
Comparison of Three and Four Element Models
-
Maxwell Diagram
-
Kelvin-Voigt Diagram
-
Standard Linear Solid Model
-
Standard Linear Solid Model 2
-
Jeffreys Rheological Model
-
Burgers Model 2
-
Burgers Model
-
Weichert Model
-
Viscoelasticity