Para-Methoxymethamphetamine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{Pharmacology-stub}} | {{Pharmacology-stub}} | ||
{{Psychoactive drug-stub}} | {{Psychoactive drug-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
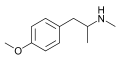
File:4-Methoxymethamphetamine.svg|Chemical structure of Para-Methoxymethamphetamine | |||
File:PMMA_tablets.jpg|Para-Methoxymethamphetamine tablets | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:01, 18 February 2025
Para-Methoxymethamphetamine (PMMA), also known as 4-methoxymethamphetamine, is a serotonin-releasing amphetamine that is related to methamphetamine and mescaline. It is often found in ecstasy tablets and is associated with severe side effects and deaths.
History[edit]
PMMA was first synthesized in the 1960s by the pharmaceutical company Upjohn but was never marketed. It reappeared on the illicit drug market in the 1990s.
Pharmacology[edit]
PMMA acts as a serotonin-releasing agent with weaker effects on dopamine and norepinephrine transporters. It also acts as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) with effects similar to mescaline.
Effects[edit]
The effects of PMMA are similar to those of MDMA (ecstasy), but it is considered more dangerous due to its higher potency, longer duration of action, and tendency to cause severe hyperthermia.
Health risks[edit]
PMMA has been associated with numerous deaths worldwide. It can cause severe hyperthermia, dehydration, seizures, heart failure, and serotonin syndrome. It is often sold as MDMA or ecstasy, increasing the risk of accidental overdose.
Legal status[edit]
PMMA is a controlled substance in many countries, including the United States, Canada, and many European countries.
See also[edit]
This article is a Psychoactive drug-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Chemical structure of Para-Methoxymethamphetamine
-
Para-Methoxymethamphetamine tablets