Sea level: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Sea_level == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Israel_Sea_Level_BW_1.JPG|Israel Sea Level BW 1 | |||
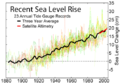
File:Recent_Sea_Level_Rise.png|Recent Sea Level Rise | |||
File:Geoida.svg|Geoida | |||
File:BadwaterSL.JPG|Badwater SL | |||
File:Mass_balance_atmospheric_circulation.png|Mass balance atmospheric circulation | |||
File:Global_sea_levels_during_the_last_Ice_Age.jpg|Global sea levels during the last Ice Age | |||
File:Glaciers_and_Sea_Level_Rise_(8742463970).jpg|Glaciers and Sea Level Rise | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:34, 23 February 2025
Sea level refers to the average level of the ocean's surface, used as a baseline for measuring elevation and depth. It is a critical factor in various areas of study, including geography, geology, meteorology, and climate change.
Measurement[edit]
Sea level is measured by both satellite and onshore gauges. Satellite altimetry provides a more accurate measurement, but onshore gauges have been in use for a longer period, providing valuable historical data.
Changes in Sea Level[edit]
Changes in sea level can be categorized as either eustatic (global) or isostatic (local). Eustatic changes are caused by an increase or decrease in the volume of water in the world's oceans, usually due to climate change. Isostatic changes are caused by the rise or fall of the land.
Effects of Climate Change[edit]
Climate change is a significant factor in sea level changes. As global temperatures rise, so do sea levels, due to the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps, and the thermal expansion of seawater.
Impact[edit]
Changes in sea level can have significant impacts on human and natural systems. These include increased flooding, damage to infrastructure, loss of land, and impacts on wildlife and ecosystems.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />