Schwannoma: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Schwannoma == | |||
<gallery> | |||
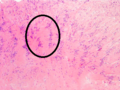
File:Schwannoma with Antoni A and Antoni B areas.jpg|Schwannoma with Antoni A and Antoni B areas | |||
File:Schwannoma - Antoni A and B - intermed mag.jpg|Schwannoma - Antoni A and B - intermediate magnification | |||
File:Peripheral schwannoma Antoni type A (2).JPG|Peripheral schwannoma Antoni type A | |||
File:Subcutaneous schwannoma (1) Antoni B.jpg|Subcutaneous schwannoma Antoni B | |||
File:Antoni A area of schwannoma with Verocay bodies - annotated.png|Antoni A area of schwannoma with Verocay bodies | |||
File:Subcutaneous schwannoma (2) Antoni B.jpg|Subcutaneous schwannoma Antoni B | |||
File:Subcutaneous schwannoma (3) Antoni B.jpg|Subcutaneous schwannoma Antoni B | |||
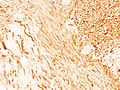
File:Subcutaneous schwannoma (4) S-100 immunostain.jpg|Subcutaneous schwannoma S-100 immunostain | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:14, 20 February 2025
Schwannoma is a type of tumor that originates from Schwann cells, the cells that produce the protective myelin sheath around peripheral nerves. Schwannomas are typically benign, meaning they are not cancerous and do not spread to other parts of the body. However, they can cause symptoms by pressing on nearby nerves or tissues.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a schwannoma can vary depending on the location of the tumor. Common symptoms can include:
Causes
The exact cause of schwannomas is not known. However, they are often associated with a genetic disorder called Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2).
Diagnosis
Schwannomas are typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as MRI or CT scan. In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
The treatment for a schwannoma depends on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health. Treatment options can include:
Prognosis
The prognosis for a person with a schwannoma is generally good, as these tumors are typically benign and do not spread to other parts of the body. However, they can cause symptoms that can affect quality of life, and treatment can sometimes lead to complications.
See also
|
|
|
Schwannoma
-
Schwannoma with Antoni A and Antoni B areas
-
Schwannoma - Antoni A and B - intermediate magnification
-
Peripheral schwannoma Antoni type A
-
Subcutaneous schwannoma Antoni B
-
Antoni A area of schwannoma with Verocay bodies
-
Subcutaneous schwannoma Antoni B
-
Subcutaneous schwannoma Antoni B
-
Subcutaneous schwannoma S-100 immunostain