Writing system: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tag: Manual revert |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
[[Category:Communication]] | [[Category:Communication]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Diagram_of_the_spoken,_written,_and_signed_modalities_of_language.svg|Diagram of the spoken, written, and signed modalities of language | |||
File:Comparison_between_single-_and_double-storey_⟨a⟩.svg|Comparison between single- and double-storey ⟨a⟩ | |||
File:Comparative_evolution_of_Cuneiform,_Egyptian_and_Chinese_characters.svg|Comparative evolution of Cuneiform, Egyptian and Chinese characters | |||
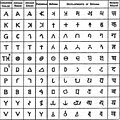
File:Sanskrit_Brhama_English_alphabets_(cropped).jpg|Sanskrit Brhama English alphabets | |||
File:Cherokee_stop_sign.png|Cherokee stop sign | |||
File:Bible_printed_with_Balinese_script.jpg|Bible printed with Balinese script | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:33, 18 February 2025
Writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable form of information storage and transfer. The processes of encoding and decoding writing systems involve shared understanding between writers and readers of the meaning behind the sets of characters that make up a script. Writing is usually recorded onto a material substance such as paper, although before paper became widely available, smooth surfaces of stone or metal were used.
History[edit]
The history of writing systems is, in many ways, the history of civilization. Ancient humans used the incising of marks on stick, bone, and stone to keep records of information. The development of writing systems came much later, with the earliest known writing systems dating back to the 4th millennium BC in the Middle East.
Types of Writing Systems[edit]
There are several types of writing systems including:
- Alphabetic writing systems - These are systems where each symbol represents a sound or a letter. Examples include the Latin alphabet used in Western languages and the Cyrillic alphabet used in Russian and other Slavic languages.
- Syllabic writing systems - In these systems, each symbol represents a syllable. Examples include the Japanese kana and the Cherokee syllabary.
- Logographic writing systems - These are systems where each symbol represents a word or a morpheme (a meaningful unit of language). Examples include Chinese characters and Egyptian hieroglyphs.
- Featural writing systems - These are systems where each symbol represents a feature, such as place or manner of articulation. Examples include the Korean Hangul and the International Phonetic Alphabet.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
|
|
|
-
Diagram of the spoken, written, and signed modalities of language
-
Comparison between single- and double-storey ⟨a⟩
-
Comparative evolution of Cuneiform, Egyptian and Chinese characters
-
Sanskrit Brhama English alphabets
-
Cherokee stop sign
-
Bible printed with Balinese script