Focal nodular hyperplasia: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
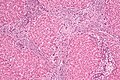
File:Focal_nodular_hyperplasia_-_intermed_mag.jpg|Focal nodular hyperplasia under intermediate magnification | |||
File:Focal_nodular_hyperplasia_liver_0521105219312.jpg|Focal nodular hyperplasia in the liver | |||
File:Liver_tumor_types_in_adults_by_relative_incidence.png|Liver tumor types in adults by relative incidence | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 04:19, 18 February 2025
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia (FNH) is a benign condition of the liver that is often discovered incidentally during imaging studies for unrelated conditions. It is the second most common benign liver lesion, with Hemangioma being the most common. FNH is more frequently found in women and is often associated with the use of oral contraceptives.
Etiology
The exact cause of FNH is not known. However, it is believed to be associated with vascular malformations in the liver. Some studies suggest a possible link with the use of oral contraceptive pills, but this has not been definitively proven.
Clinical Presentation
Most patients with FNH are asymptomatic. When symptoms do occur, they are usually nonspecific and may include abdominal discomfort or fullness. Rarely, a large FNH can cause significant symptoms due to mass effect.
Diagnosis
FNH is often discovered incidentally during imaging studies for unrelated conditions. The diagnosis can usually be made based on characteristic imaging findings on Ultrasound, CT, or MRI. In some cases, a liver biopsy may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
No treatment is usually necessary for FNH, as it is a benign condition and does not increase the risk of liver cancer. In rare cases where the FNH is large and causing symptoms, surgical resection may be considered.
Prognosis
The prognosis for FNH is excellent. It does not increase the risk of liver cancer and does not usually require treatment.