Corundum: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Several_corundum_crystals.jpg|Several corundum crystals | |||
File:Corindon_azulEZ.jpg|Blue corundum | |||
File:Corundum.png|Corundum | |||
File:Corundum-pV.svg|Corundum | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:45, 18 February 2025
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide (Al2O3) typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is one of the naturally transparent materials, but can have different colors when impurities are present. Transparent specimens are used as gems, called ruby if red and sapphire if any other color.
Properties[edit]
Corundum has two primary gem varieties: ruby and sapphire. Rubies are red due to the presence of chromium, and sapphires exhibit a range of colors depending on what transition metal is present. A rare type of sapphire, padparadscha sapphire, is pink-orange.
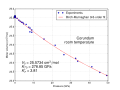
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness characterizes the scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of a harder material to scratch a softer material. Corundum has a hardness of 9 on the Mohs scale, making it among the hardest minerals.
Occurrence[edit]
Corundum is commonly found in metamorphic rocks such as gneiss and mica schist. It also occurs in igneous rocks and in certain types of meteorites.
Uses[edit]
Corundum is used as an abrasive because it has a hardness second only to diamond. It is also used in the manufacture of sandpaper and grinding wheels. Gem-quality corundum is also used in jewelry, with different varieties such as ruby and sapphire being highly prized.