Clinical neurochemistry: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Neuron_with_mHtt_inclusion.jpg|Neuron with mHtt inclusion | |||
File:Efficacy_spectrum.png|Efficacy spectrum | |||
File:DoseResponse000.jpg|Dose response curve | |||
File:Sleep_EEG_REM.png|Sleep EEG REM | |||
File:Functional_magnetic_resonance_imaging.jpg|Functional magnetic resonance imaging | |||
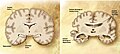
File:Alzheimer's_disease_brain_comparison.jpg|Alzheimer's disease brain comparison | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 18 February 2025
Clinical neurochemistry is a branch of neuroscience that explores the chemical processes and compounds that are involved in the nervous system. It is a vital field in understanding the function and dysfunction of the brain and nervous system.
Overview[edit]
Clinical neurochemistry involves the study of neurons and glial cells, the two main types of cells in the nervous system. Neurons are responsible for transmitting signals, while glial cells provide support and protection for neurons. The chemical processes that occur in these cells, including the production and use of neurotransmitters, are a key focus of clinical neurochemistry.
Neurotransmitters[edit]
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another 'target' neuron, or to an effector cell. They play a crucial role in the transmission of signals in the nervous system. Some of the most well-known neurotransmitters include serotonin, dopamine, and acetylcholine.
Disorders[edit]
Disruptions in the chemical processes of the nervous system can lead to various neurological and psychiatric disorders. For example, an imbalance in neurotransmitters can lead to conditions such as depression, schizophrenia, and Parkinson's disease. Clinical neurochemistry, therefore, plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of these conditions.
Research and Future Directions[edit]
Research in clinical neurochemistry is ongoing, with scientists continually discovering new aspects of the nervous system's chemical processes. This research is crucial for the development of new treatments for neurological and psychiatric disorders.