Stylohyoid muscle: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Stylohyoid muscle == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Musculi_colli_stylohyoideus.svg|Muscles of the neck, including the stylohyoid muscle | |||
File:Stylohyoid_muscle.PNG|Stylohyoid muscle | |||
File:Gray137.png|Muscles of the neck, anterior view | |||
File:Gray186.png|Muscles of the neck, lateral view | |||
File:Gray507.png|Muscles of the neck, deep dissection | |||
File:Stylohyoideus.png|Stylohyoid muscle | |||
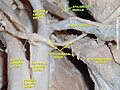
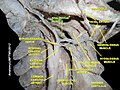
File:Slide6aaa.JPG|Stylohyoid muscle | |||
File:Slide18aaa.JPG|Stylohyoid muscle | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:14, 18 February 2025
Stylohyoid muscle is a slender muscle in the human anatomy that belongs to the suprahyoid muscles group. It is named for its two attachments: the styloid process of the temporal bone and the hyoid bone.
Etymology[edit]
The term "stylohyoid" is derived from the Greek words "stylos" meaning pillar and "hyoeides" meaning shaped like the letter upsilon.
Structure[edit]
The stylohyoid muscle originates from the back of the styloid process of the temporal bone and inserts into the body of the hyoid bone. It is innervated by the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII).
Function[edit]
The primary function of the stylohyoid muscle is to elevate and retract the hyoid bone, aiding in swallowing and speech.
Clinical significance[edit]
Anomalies of the stylohyoid muscle can lead to a condition known as Eagle's syndrome, characterized by recurrent pain in the throat and difficulty swallowing.
Related terms[edit]
See also[edit]
|
|
|
Stylohyoid muscle[edit]
-
Muscles of the neck, including the stylohyoid muscle
-
Stylohyoid muscle
-
Muscles of the neck, anterior view
-
Muscles of the neck, lateral view
-
Muscles of the neck, deep dissection
-
Stylohyoid muscle
-
Stylohyoid muscle
-
Stylohyoid muscle