Homotaurine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[Category:GABA analogues]] | [[Category:GABA analogues]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Homotaurine == | == Homotaurine == | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 23:49, 16 March 2025
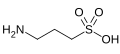
Homotaurine (also known as Tramiprosate) is a natural compound found in various species of red algae. It is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue and has been used as a nutritional supplement due to its potential neuroprotective properties.
History[edit]
Homotaurine was first isolated from the red algae Ceramium rubrum and Gracilaria verrucosa. It was initially studied for its potential to inhibit fibrosis in the liver. Later, it was found to have potential benefits in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Biochemistry[edit]
Homotaurine is a GABA analogue, meaning it has a similar structure to the neurotransmitter GABA. It is believed to work by binding to glutamate receptors in the brain, which may help to reduce the overexcitation of neurons that can lead to neurodegeneration.
Medical Uses[edit]
Homotaurine has been studied for its potential use in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It is believed to work by inhibiting the aggregation of amyloid-beta peptides, which are a major component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of Alzheimer's patients.
Side Effects[edit]
As with any supplement, homotaurine can have side effects. These may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. It is always recommended to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
Homotaurine[edit]
-
Homotaurine
-
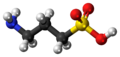
Homotaurine 3D Model