Diseases of the foot: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{short description|Overview of diseases affecting the foot}} | ||
{{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | {{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The human foot is a complex structure composed of bones, | The human foot is a complex structure composed of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, all working together to support the body and enable movement. [[Diseases of the foot]] can affect any of these components, leading to pain, discomfort, and impaired mobility. This article provides an overview of common foot diseases, their causes, symptoms, and potential treatments. | ||
== | ==Common Foot Diseases== | ||
== | ===Flatfoot=== | ||
[[File:Adult_Flatfoot.JPG|thumb|right|An example of adult flatfoot.]] | |||
Flatfoot, or pes planus, is a condition where the arch of the foot collapses, resulting in the entire sole coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. It can be congenital or acquired, often due to posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and difficulty walking. | |||
=== | ===Ischemia=== | ||
[[ | [[File:Ischemia_rotate.jpg|thumb|left|Ischemic foot showing signs of poor blood circulation.]] | ||
Ischemia of the foot occurs when there is insufficient blood flow to the tissues, often due to peripheral artery disease. This can lead to pain, ulcers, and in severe cases, gangrene. Management includes improving circulation through lifestyle changes, medication, or surgical intervention. | |||
=== | ===Chilblains=== | ||
[[File:Wintertenen.jpg|thumb|right|Chilblains on the toes.]] | |||
Chilblains, or pernio, are small, itchy, and painful swellings on the skin that occur as a reaction to cold temperatures. They typically affect the toes and can be managed by keeping the feet warm and dry. | |||
=== | ===Hallux Valgus=== | ||
[[ | [[File:Hallux_valgus_und_Krallenzehe_II_(präop.).jpg|thumb|left|Preoperative image of hallux valgus and claw toe.]] | ||
Hallux valgus, commonly known as a bunion, is a deformity of the big toe joint, causing the toe to deviate towards the other toes. It can lead to pain and difficulty wearing shoes. Treatment options include orthotics, physical therapy, and surgery. | |||
===Athlete's Foot=== | ===Athlete's Foot=== | ||
[[ | [[File:Athletes_foot.JPG|thumb|right|Fungal infection characteristic of athlete's foot.]] | ||
Athlete's foot, or tinea pedis, is a fungal infection that affects the skin of the feet, particularly between the toes. It is characterized by itching, scaling, and redness. Antifungal treatments are effective in managing the condition. | |||
== | ===Leprosy=== | ||
[[File:ASC_Leiden_-_Coutinho_Collection_-_11_02_-_Ziguinchor_hospital,_Senegal_-_1973.tif|thumb|left|Foot affected by leprosy.]] | |||
Leprosy, caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae, can lead to nerve damage and deformities in the feet. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics can prevent severe complications. | |||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention and Management== | ||
Preventing foot diseases involves maintaining good foot hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear, and managing underlying health conditions such as diabetes and vascular disease. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help in early detection and management of foot problems. | |||
==Related Pages== | ==Related Pages== | ||
* [[ | * [[Foot anatomy]] | ||
* [[Podiatry]] | * [[Podiatry]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Peripheral artery disease]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Diabetes and foot care]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Diseases of the foot]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Musculoskeletal disorders]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Skin conditions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:19, 21 February 2025
Overview of diseases affecting the foot
Overview[edit]
The human foot is a complex structure composed of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, all working together to support the body and enable movement. Diseases of the foot can affect any of these components, leading to pain, discomfort, and impaired mobility. This article provides an overview of common foot diseases, their causes, symptoms, and potential treatments.
Common Foot Diseases[edit]
Flatfoot[edit]

Flatfoot, or pes planus, is a condition where the arch of the foot collapses, resulting in the entire sole coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. It can be congenital or acquired, often due to posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and difficulty walking.
Ischemia[edit]

Ischemia of the foot occurs when there is insufficient blood flow to the tissues, often due to peripheral artery disease. This can lead to pain, ulcers, and in severe cases, gangrene. Management includes improving circulation through lifestyle changes, medication, or surgical intervention.
Chilblains[edit]

Chilblains, or pernio, are small, itchy, and painful swellings on the skin that occur as a reaction to cold temperatures. They typically affect the toes and can be managed by keeping the feet warm and dry.
Hallux Valgus[edit]
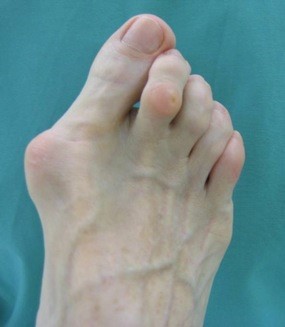
Hallux valgus, commonly known as a bunion, is a deformity of the big toe joint, causing the toe to deviate towards the other toes. It can lead to pain and difficulty wearing shoes. Treatment options include orthotics, physical therapy, and surgery.
Athlete's Foot[edit]

Athlete's foot, or tinea pedis, is a fungal infection that affects the skin of the feet, particularly between the toes. It is characterized by itching, scaling, and redness. Antifungal treatments are effective in managing the condition.
Leprosy[edit]

Leprosy, caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae, can lead to nerve damage and deformities in the feet. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics can prevent severe complications.
Prevention and Management[edit]
Preventing foot diseases involves maintaining good foot hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear, and managing underlying health conditions such as diabetes and vascular disease. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help in early detection and management of foot problems.