Aldol condensation: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
* [[Organic synthesis]] | * [[Organic synthesis]] | ||
* [[Claisen condensation]] | * [[Claisen condensation]] | ||
[[Category:Organic reactions]] | [[Category:Organic reactions]] | ||
[[Category:Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions]] | [[Category:Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:35, 18 February 2025
A chemical reaction involving the formation of a _-hydroxy ketone or aldehyde
Aldol condensation is an important organic reaction in which an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form a _-hydroxy ketone or aldehyde, followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone. This reaction is a key step in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds in organic synthesis.
Mechanism[edit]
The aldol condensation can proceed via either a base-catalyzed or an acid-catalyzed mechanism.
Base-catalyzed mechanism[edit]
In the base-catalyzed aldol condensation, a base such as hydroxide or an alkoxide ion abstracts a proton from the _-carbon of a carbonyl compound, generating an enolate ion. This enolate ion then attacks the carbonyl carbon of another molecule, forming a _-hydroxy ketone or aldehyde. Subsequent dehydration leads to the formation of an _,_-unsaturated carbonyl compound.

Acid-catalyzed mechanism[edit]
In the acid-catalyzed aldol condensation, the carbonyl compound is protonated, making it more electrophilic. An enol form of the carbonyl compound then attacks the protonated carbonyl group, leading to the formation of a _-hydroxy ketone or aldehyde. Dehydration occurs to yield the _,_-unsaturated carbonyl compound.

Examples[edit]
A classic example of an aldol condensation is the reaction between acetaldehyde molecules to form crotonaldehyde.

Applications[edit]
Aldol condensations are widely used in the synthesis of complex molecules, including natural products and pharmaceuticals. They are also employed in industrial processes, such as the production of pentaerythritol, a key component in the manufacture of alkyd resins.
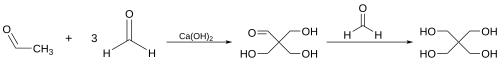
Variations[edit]
Several variations of the aldol condensation exist, including the Henry reaction, the Robinson annulation, and the Claisen-Schmidt condensation. These variations expand the scope and utility of the aldol reaction in organic synthesis.