Hip fracture: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hip fracture | |||
| image = [[File:Cdm_hip_fracture_343.jpg|250px]] | |||
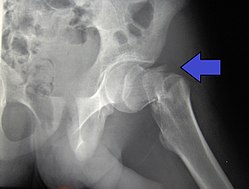
| caption = X-ray of a [[hip fracture]] | |||
| field = [[Orthopedic surgery]] | |||
| synonyms = [[Femoral neck fracture]], [[intertrochanteric fracture]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Pain]] in the [[hip]] or [[groin]], inability to [[walk]] | |||
| complications = [[Deep vein thrombosis]], [[pulmonary embolism]], [[pneumonia]], [[pressure ulcers]] | |||
| onset = Sudden | |||
| duration = Varies | |||
| causes = [[Osteoporosis]], [[trauma]] | |||
| risks = [[Old age]], [[osteoporosis]], [[falls]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[X-ray]], [[CT scan]] | |||
| differential = [[Hip dislocation]], [[pelvic fracture]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[physical therapy]] | |||
| medication = [[Pain management]], [[anticoagulants]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies, often good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in the elderly | |||
}} | |||
[[File:X-ray_of_subtle_compressive_hip_fracture,_labeled.jpg|left|thumb|X-ray of subtle compressive hip fracture]] | |||
[[File:CT_of_subtle_compressive_hip_fracture.jpg|left|thumb|CT of subtle compressive hip fracture]] | |||
[[File:T1_TSE_MRI_of_hip_fracture.jpg|left|thumb|T1 TSE MRI of hip fracture]] | |||
[[File:Hip_fracture_classification.png|thumb|Hip fracture classification]] | |||
[[File:Shf_ohne_dislokation_medial_ap.jpg|left|thumb|Hip fracture]] | |||
[[File:Skin_folds_close_to_a_hip_fracture_(with_arrows).jpg|thumb|Skin folds close to a hip fracture]] | |||
[[File:Shf_medial_verschraubt_crop.jpg|left|thumb|Hip fracture]] | |||
[[File:Cdm_hip_implant_348.jpg|thumb|Hip fracture]] | |||
[[File:Hip_fracture_incidence_world_map.svg|thumb|Hip fracture incidence world map]] | |||
'''Hip fracture''' is a serious injury that occurs when there is a break in the [[femur]] (thigh bone) near the [[hip joint]]. It is most commonly caused by [[falls]] or [[trauma]], and is particularly common in older people due to [[osteoporosis]]. | '''Hip fracture''' is a serious injury that occurs when there is a break in the [[femur]] (thigh bone) near the [[hip joint]]. It is most commonly caused by [[falls]] or [[trauma]], and is particularly common in older people due to [[osteoporosis]]. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Hip fractures are most often caused by a fall, particularly in older people. Other causes can include [[trauma]] such as a car accident, or a disease that weakens the bones, such as [[osteoporosis]] or [[cancer]]. | Hip fractures are most often caused by a fall, particularly in older people. Other causes can include [[trauma]] such as a car accident, or a disease that weakens the bones, such as [[osteoporosis]] or [[cancer]]. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The most common symptoms of a hip fracture include: | The most common symptoms of a hip fracture include: | ||
| Line 10: | Line 37: | ||
* Swelling or bruising in the hip area | * Swelling or bruising in the hip area | ||
* Shortening of the leg or turning outward of the leg | * Shortening of the leg or turning outward of the leg | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
A hip fracture is usually diagnosed through a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. These can include [[X-ray]]s, [[CT scan]]s, or [[MRI]]s. In some cases, a [[bone scan]] may be used to identify stress fractures. | A hip fracture is usually diagnosed through a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. These can include [[X-ray]]s, [[CT scan]]s, or [[MRI]]s. In some cases, a [[bone scan]] may be used to identify stress fractures. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for a hip fracture usually involves surgery to repair the break. This can involve using metal screws to hold the bone together ([[internal fixation]]), replacing part of the femur ([[partial hip replacement]]), or replacing the entire hip joint ([[total hip replacement]]). After surgery, [[physical therapy]] is often needed to help regain strength and mobility. | Treatment for a hip fracture usually involves surgery to repair the break. This can involve using metal screws to hold the bone together ([[internal fixation]]), replacing part of the femur ([[partial hip replacement]]), or replacing the entire hip joint ([[total hip replacement]]). After surgery, [[physical therapy]] is often needed to help regain strength and mobility. | ||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
Prevention of hip fractures involves reducing the risk of falls and treating underlying conditions that weaken the bone. This can include: | Prevention of hip fractures involves reducing the risk of falls and treating underlying conditions that weaken the bone. This can include: | ||
| Line 22: | Line 46: | ||
* Medication to treat osteoporosis | * Medication to treat osteoporosis | ||
* Using assistive devices such as canes or walkers | * Using assistive devices such as canes or walkers | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Osteoporosis]] | * [[Osteoporosis]] | ||
* [[Fall prevention]] | * [[Fall prevention]] | ||
* [[Physical therapy]] | * [[Physical therapy]] | ||
[[Category:Orthopedic problems]] | [[Category:Orthopedic problems]] | ||
[[Category:Geriatrics]] | [[Category:Geriatrics]] | ||
[[Category:Injuries]] | [[Category:Injuries]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 12:07, 14 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hip fracture | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Femoral neck fracture, intertrochanteric fracture |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Pain in the hip or groin, inability to walk |
| Complications | Deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, pneumonia, pressure ulcers |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Osteoporosis, trauma |
| Risks | Old age, osteoporosis, falls |
| Diagnosis | X-ray, CT scan |
| Differential diagnosis | Hip dislocation, pelvic fracture |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, physical therapy |
| Medication | Pain management, anticoagulants |
| Prognosis | Varies, often good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common in the elderly |
| Deaths | N/A |









Hip fracture is a serious injury that occurs when there is a break in the femur (thigh bone) near the hip joint. It is most commonly caused by falls or trauma, and is particularly common in older people due to osteoporosis.
Causes[edit]
Hip fractures are most often caused by a fall, particularly in older people. Other causes can include trauma such as a car accident, or a disease that weakens the bones, such as osteoporosis or cancer.
Symptoms[edit]
The most common symptoms of a hip fracture include:
- Severe pain in the hip or groin
- Inability to move or lift the leg
- Swelling or bruising in the hip area
- Shortening of the leg or turning outward of the leg
Diagnosis[edit]
A hip fracture is usually diagnosed through a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. These can include X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs. In some cases, a bone scan may be used to identify stress fractures.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for a hip fracture usually involves surgery to repair the break. This can involve using metal screws to hold the bone together (internal fixation), replacing part of the femur (partial hip replacement), or replacing the entire hip joint (total hip replacement). After surgery, physical therapy is often needed to help regain strength and mobility.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of hip fractures involves reducing the risk of falls and treating underlying conditions that weaken the bone. This can include:
- Regular exercise to improve balance and strength
- Medication to treat osteoporosis
- Using assistive devices such as canes or walkers


