Tropic acid: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
File:Phenylhydracrylic_acid.svg | File:Phenylhydracrylic_acid.svg | ||
File:Tropicacidsynthesis1.svg | File:Tropicacidsynthesis1.svg | ||
</gallery> | |||
== Tropic_acid == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Phenylhydracrylic_acid.svg|Phenylhydracrylic acid structure | |||
File:Tropicacidsynthesis1.svg|Tropic acid synthesis pathway | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:53, 18 February 2025
Tropic Acid[edit]
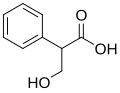
Tropic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula C9H10O3. It is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in water and alcohol. Tropic acid is a chiral molecule and exists in two enantiomeric forms. It is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of atropine and other tropane alkaloids.
Structure and Properties[edit]
Tropic acid consists of a phenyl group attached to a 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoic acid backbone. The presence of the hydroxyl group and the carboxylic acid group makes it a versatile compound in organic synthesis. The compound is optically active due to the presence of a chiral center at the carbon atom bearing the hydroxyl group.
Synthesis[edit]
Tropic acid can be synthesized through several methods. One common method involves the reaction of phenylacetic acid with acetaldehyde in the presence of a base, followed by oxidation. Another method involves the use of phenylhydracrylic acid as a starting material, which undergoes a series of reactions to yield tropic acid.


Applications[edit]
Tropic acid is primarily used in the synthesis of atropine, a medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings, as well as some types of slow heart rate. It is also used in the synthesis of other tropane alkaloids, which have various pharmacological effects.
Related Compounds[edit]
Tropic acid is related to several other compounds, including tropine, tropinone, and atropine. These compounds share a common tropane ring structure and are important in the field of medicinal chemistry.
Related Pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
Tropic acid[edit]
Tropic_acid[edit]
-
Phenylhydracrylic acid structure
-
Tropic acid synthesis pathway