Acute uric acid nephropathy: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{SI}} {{Infobox medical condition | ||
| name = Acute uric acid nephropathy | |||
| image = [[File:Uric_acid_crystals.jpg|250px]] | |||
[[File:Uric acid crystals | | caption = Uric acid crystals | ||
| field = [[Nephrology]] | |||
| synonyms = | |||
| symptoms = [[Oliguria]], [[anuria]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[edema]], [[hypertension]] | |||
| complications = [[Acute kidney injury]], [[chronic kidney disease]] | |||
| onset = Sudden | |||
| duration = | |||
| causes = [[Tumor lysis syndrome]], high [[uric acid]] levels | |||
| risks = [[Chemotherapy]], [[hematologic malignancies]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Blood test]], [[urinalysis]], [[renal ultrasound]] | |||
| differential = [[Acute tubular necrosis]], [[chronic kidney disease]] | |||
| treatment = [[Hydration]], [[allopurinol]], [[rasburicase]], [[dialysis]] | |||
| medication = [[Allopurinol]], [[rasburicase]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depending on severity and treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
| deaths = | |||
}} | |||
'''Acute uric acid nephropathy''' is a medical condition characterized by the rapid deterioration of kidney function due to the accumulation of [[uric acid]] in the renal tubules. This condition is often associated with [[tumor lysis syndrome]], a complication that can occur after the treatment of certain cancers. | '''Acute uric acid nephropathy''' is a medical condition characterized by the rapid deterioration of kidney function due to the accumulation of [[uric acid]] in the renal tubules. This condition is often associated with [[tumor lysis syndrome]], a complication that can occur after the treatment of certain cancers. | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
[[File:Kidney and adrenal gland.jpg|Kidney and adrenal gland|thumb]] | [[File:Kidney and adrenal gland.jpg|Kidney and adrenal gland|thumb]] | ||
The pathophysiology of acute uric acid nephropathy involves the precipitation of uric acid crystals in the renal tubules. Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of [[purines]], which are found in many foods and are also released during the rapid turnover of cells, such as in [[leukemia]] or [[lymphoma]]. When the concentration of uric acid in the blood becomes excessively high, it can crystallize and obstruct the renal tubules, leading to acute kidney injury. | The pathophysiology of acute uric acid nephropathy involves the precipitation of uric acid crystals in the renal tubules. Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of [[purines]], which are found in many foods and are also released during the rapid turnover of cells, such as in [[leukemia]] or [[lymphoma]]. When the concentration of uric acid in the blood becomes excessively high, it can crystallize and obstruct the renal tubules, leading to acute kidney injury. | ||
==Clinical presentation== | ==Clinical presentation== | ||
Patients with acute uric acid nephropathy typically present with symptoms of acute kidney injury, which may include decreased urine output, elevated serum creatinine, and electrolyte imbalances. The condition is often precipitated by the initiation of chemotherapy in patients with high tumor burdens, leading to the rapid release of intracellular contents, including uric acid. | Patients with acute uric acid nephropathy typically present with symptoms of acute kidney injury, which may include decreased urine output, elevated serum creatinine, and electrolyte imbalances. The condition is often precipitated by the initiation of chemotherapy in patients with high tumor burdens, leading to the rapid release of intracellular contents, including uric acid. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
The diagnosis of acute uric acid nephropathy is based on clinical presentation, laboratory findings, and imaging studies. Laboratory tests may reveal hyperuricemia, elevated serum creatinine, and metabolic acidosis. Imaging studies, such as an ultrasound of the kidneys, may show signs of renal obstruction or swelling. | The diagnosis of acute uric acid nephropathy is based on clinical presentation, laboratory findings, and imaging studies. Laboratory tests may reveal hyperuricemia, elevated serum creatinine, and metabolic acidosis. Imaging studies, such as an ultrasound of the kidneys, may show signs of renal obstruction or swelling. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
[[File:Allopurinol.png|thumb| | [[File:Allopurinol.png|thumb|left|Chemical structure of allopurinol, a medication used to reduce uric acid levels.]] | ||
The primary goal of treatment is to reduce serum uric acid levels and alleviate renal obstruction. This can be achieved through the use of medications such as [[allopurinol]] or [[rasburicase]], which help to lower uric acid levels. In addition, aggressive hydration and alkalinization of the urine may be employed to prevent further crystal formation. In severe cases, dialysis may be necessary to support kidney function. | The primary goal of treatment is to reduce serum uric acid levels and alleviate renal obstruction. This can be achieved through the use of medications such as [[allopurinol]] or [[rasburicase]], which help to lower uric acid levels. In addition, aggressive hydration and alkalinization of the urine may be employed to prevent further crystal formation. In severe cases, dialysis may be necessary to support kidney function. | ||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
Preventive measures are crucial in patients at high risk for acute uric acid nephropathy, particularly those undergoing chemotherapy for malignancies with high cell turnover. Prophylactic administration of allopurinol and adequate hydration before the initiation of chemotherapy can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. | Preventive measures are crucial in patients at high risk for acute uric acid nephropathy, particularly those undergoing chemotherapy for malignancies with high cell turnover. Prophylactic administration of allopurinol and adequate hydration before the initiation of chemotherapy can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis of acute uric acid nephropathy depends on the promptness of diagnosis and treatment. With early intervention, kidney function can often be preserved, and the risk of long-term complications minimized. However, delayed treatment may lead to irreversible kidney damage. | The prognosis of acute uric acid nephropathy depends on the promptness of diagnosis and treatment. With early intervention, kidney function can often be preserved, and the risk of long-term complications minimized. However, delayed treatment may lead to irreversible kidney damage. | ||
==See also== | |||
== | |||
* [[Tumor lysis syndrome]] | * [[Tumor lysis syndrome]] | ||
* [[Acute kidney injury]] | * [[Acute kidney injury]] | ||
* [[Hyperuricemia]] | * [[Hyperuricemia]] | ||
[[Category:Nephrology]] | [[Category:Nephrology]] | ||
[[Category:Kidney diseases]] | [[Category:Kidney diseases]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:13, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Acute uric acid nephropathy | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Oliguria, anuria, nausea, vomiting, edema, hypertension |
| Complications | Acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Tumor lysis syndrome, high uric acid levels |
| Risks | Chemotherapy, hematologic malignancies |
| Diagnosis | Blood test, urinalysis, renal ultrasound |
| Differential diagnosis | Acute tubular necrosis, chronic kidney disease |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Hydration, allopurinol, rasburicase, dialysis |
| Medication | Allopurinol, rasburicase |
| Prognosis | Variable, depending on severity and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | |
Acute uric acid nephropathy is a medical condition characterized by the rapid deterioration of kidney function due to the accumulation of uric acid in the renal tubules. This condition is often associated with tumor lysis syndrome, a complication that can occur after the treatment of certain cancers.
Pathophysiology[edit]

The pathophysiology of acute uric acid nephropathy involves the precipitation of uric acid crystals in the renal tubules. Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of purines, which are found in many foods and are also released during the rapid turnover of cells, such as in leukemia or lymphoma. When the concentration of uric acid in the blood becomes excessively high, it can crystallize and obstruct the renal tubules, leading to acute kidney injury.
Clinical presentation[edit]
Patients with acute uric acid nephropathy typically present with symptoms of acute kidney injury, which may include decreased urine output, elevated serum creatinine, and electrolyte imbalances. The condition is often precipitated by the initiation of chemotherapy in patients with high tumor burdens, leading to the rapid release of intracellular contents, including uric acid.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of acute uric acid nephropathy is based on clinical presentation, laboratory findings, and imaging studies. Laboratory tests may reveal hyperuricemia, elevated serum creatinine, and metabolic acidosis. Imaging studies, such as an ultrasound of the kidneys, may show signs of renal obstruction or swelling.
Treatment[edit]
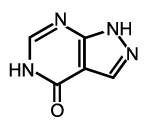
The primary goal of treatment is to reduce serum uric acid levels and alleviate renal obstruction. This can be achieved through the use of medications such as allopurinol or rasburicase, which help to lower uric acid levels. In addition, aggressive hydration and alkalinization of the urine may be employed to prevent further crystal formation. In severe cases, dialysis may be necessary to support kidney function.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures are crucial in patients at high risk for acute uric acid nephropathy, particularly those undergoing chemotherapy for malignancies with high cell turnover. Prophylactic administration of allopurinol and adequate hydration before the initiation of chemotherapy can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis of acute uric acid nephropathy depends on the promptness of diagnosis and treatment. With early intervention, kidney function can often be preserved, and the risk of long-term complications minimized. However, delayed treatment may lead to irreversible kidney damage.