Accuracy and precision: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
=== Accuracy === | === Accuracy === | ||
Accuracy refers to the closeness of a measured value to a standard or known value. In other words, it is the degree to which the result of a measurement conforms to the correct value or a standard. Accuracy is often expressed as a percentage, indicating how close the measurement is to the true value. | Accuracy refers to the closeness of a measured value to a standard or known value. In other words, it is the degree to which the result of a measurement conforms to the correct value or a standard. Accuracy is often expressed as a percentage, indicating how close the measurement is to the true value. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
== Relationship between Accuracy and Precision == | == Relationship between Accuracy and Precision == | ||
[[File:High precision Low accuracy.svg|thumb|right|High precision, low accuracy.]] | [[File:High precision Low accuracy.svg|thumb|right|High precision, low accuracy.]] | ||
Accuracy and precision are independent of each other. A measurement system can be: | Accuracy and precision are independent of each other. A measurement system can be: | ||
| Line 53: | Line 50: | ||
[[Category:Measurement]] | [[Category:Measurement]] | ||
[[Category:Statistics]] | [[Category:Statistics]] | ||
== Accuracy and Precision == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Accuracy_and_precision.svg|Accuracy and precision | |||
File:Accuracy_(trueness_and_precision).svg|Accuracy (trueness and precision) | |||
File:High_accuracy_Low_precision.svg|High accuracy, low precision | |||
File:High_precision_Low_accuracy.svg|High precision, low accuracy | |||
File:ACCvsPrecision.jpg|Accuracy and Precision | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:04, 18 February 2025
Accuracy and Precision[edit]

Accuracy and precision are two important concepts in the field of measurement and statistics. They are often used to describe the quality of a measurement system or the results of a measurement process.
Definitions[edit]
Accuracy[edit]
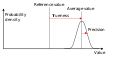
Accuracy refers to the closeness of a measured value to a standard or known value. In other words, it is the degree to which the result of a measurement conforms to the correct value or a standard. Accuracy is often expressed as a percentage, indicating how close the measurement is to the true value.
Precision[edit]
Precision, on the other hand, refers to the closeness of two or more measurements to each other. It is a measure of the repeatability or reproducibility of the measurement process. High precision means that repeated measurements under unchanged conditions show the same results.
Relationship between Accuracy and Precision[edit]

Accuracy and precision are independent of each other. A measurement system can be:
- High accuracy, low precision: Measurements are close to the true value but not to each other.
- Low accuracy, high precision: Measurements are close to each other but not to the true value.
- High accuracy, high precision: Measurements are both close to the true value and to each other.
- Low accuracy, low precision: Measurements are neither close to the true value nor to each other.
Importance in Measurement[edit]
In scientific research and engineering, both accuracy and precision are crucial for ensuring the reliability and validity of results. Accurate and precise measurements are essential for making informed decisions and for the advancement of knowledge.
Factors Affecting Accuracy and Precision[edit]
Several factors can affect the accuracy and precision of measurements, including:
Related Pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Comparison of accuracy and precision.
Accuracy and Precision[edit]
-
Accuracy and precision
-
Accuracy (trueness and precision)
-
High accuracy, low precision
-
High precision, low accuracy
-
Accuracy and Precision