4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category:Opioids]] | [[Category:Opioids]] | ||
[[Category:Synthetic opioids]] | [[Category:Synthetic opioids]] | ||
== 4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl == | |||
<gallery> | |||
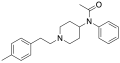
File:4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl_Structure.svg|Chemical structure of 4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl | |||
File:Acetylfentanyl-4-methylphenethyl.png|4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:34, 18 February 2025
4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl[edit]

4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl is a synthetic opioid analgesic that is structurally related to fentanyl. It is part of a class of drugs known as fentanyl analogs, which are designed to mimic the effects of fentanyl, a potent opioid used in pain management and anesthesia.
Chemical Structure[edit]
4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl is characterized by the presence of a 4-methylphenethyl group attached to the acetylfentanyl core structure. This modification is responsible for its unique pharmacological properties compared to other fentanyl analogs.
Pharmacology[edit]
As with other opioids, 4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl acts primarily on the mu-opioid receptor in the central nervous system. This interaction results in analgesic effects, as well as the potential for euphoria, respiratory depression, and physical dependence.
Legal Status[edit]
Due to its potential for abuse and lack of medical use, 4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl is classified as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions. It is often included in the list of substances banned under analog drug laws, which aim to control substances that are chemically similar to already regulated drugs.
Synthesis[edit]
The synthesis of 4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl involves the modification of the fentanyl structure by introducing a 4-methylphenethyl group. This process requires advanced knowledge of organic chemistry and access to specific chemical reagents and equipment.
Health Risks[edit]
The use of 4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl carries significant health risks, including the potential for overdose and death. The potency of fentanyl analogs can vary widely, making it difficult to determine a safe dosage. Overdose symptoms may include severe respiratory depression, loss of consciousness, and death.
Related Pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Chemical structure of Acetylfentanyl-4-methylphenethyl
4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl[edit]
-
Chemical structure of 4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl
-
4-Methylphenethylacetylfentanyl