Bradykinin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Bradykinin == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Bradykinin_structure.svg|Bradykinin structure | |||
File:Bradykinin_updated.png|Bradykinin updated | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 19:11, 16 March 2025
Bradykinin is a peptide that causes blood vessels to dilate (enlarge), and therefore causes blood pressure to fall. It is a part of the kallikrein-kinin system, which is a complex system of blood proteins that play a role in inflammation, blood pressure control, coagulation, and pain.
Structure and Function[edit]
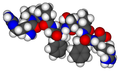
Bradykinin is a nonapeptide, meaning it is composed of nine amino acids. The sequence of these amino acids is Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg. Bradykinin is produced from a precursor protein called kininogen through the action of the enzyme kallikrein.
Physiological Role[edit]
Bradykinin is involved in several physiological processes:
- **Vasodilation**: It causes the dilation of blood vessels, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure.
- **Pain**: Bradykinin is known to induce pain by stimulating sensory neurons.
- **Inflammation**: It plays a significant role in the inflammatory response by increasing the permeability of blood vessels, allowing immune cells to reach the site of infection or injury.
- **Smooth Muscle Contraction**: It can cause the contraction of smooth muscle in the bronchi and gastrointestinal tract.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Bradykinin is implicated in several pathological conditions:
- **Hereditary Angioedema**: A genetic disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of severe swelling. This condition is often due to a deficiency in C1 inhibitor, which normally regulates the production of bradykinin.
- **Septic Shock**: Excessive production of bradykinin can contribute to the severe drop in blood pressure seen in septic shock.
- **Chronic Pain**: Elevated levels of bradykinin are associated with chronic pain conditions.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Bradykinin levels can be influenced by certain medications:
- **ACE Inhibitors**: These drugs, used to treat high blood pressure, can increase bradykinin levels by inhibiting its breakdown, which can sometimes lead to a side effect known as ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema.
- **Kininase Inhibitors**: These are experimental drugs that aim to modulate the effects of bradykinin for therapeutic purposes.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
External Links[edit]
Bradykinin[edit]
-
Bradykinin structure
-
Bradykinin updated