Trolox: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
__NOINDEX__ | __NOINDEX__ | ||
== Trolox == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Trolox.png|Trolox | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:08, 17 March 2025
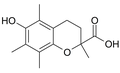
Trolox is a water-soluble analog of Vitamin E, a type of antioxidant. It is often used in scientific research to assess the antioxidant capacity of various substances.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Trolox is a derivative of chroman, a type of organic compound. It has a carboxylic acid group in place of the phytyl tail found in natural Vitamin E. This modification makes Trolox more soluble in water than Vitamin E.
Uses[edit]
Trolox is primarily used in scientific research. It serves as a reference standard in antioxidant assays, such as the Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) assay. In this assay, the antioxidant capacity of a substance is compared to that of Trolox, with the results expressed in Trolox equivalents.
Safety[edit]
As a derivative of Vitamin E, Trolox is generally considered safe. However, like all substances, it can cause adverse effects if used improperly. Always follow safety guidelines when handling Trolox.