Bohrium: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
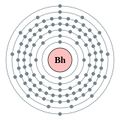
Bohrium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Bh and atomic number 107. It is a member of the [[transition metals]] and is part of the [[7th period]] in the [[periodic table]]. Bohrium is named after the Danish physicist [[Niels Bohr]], who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory. | Bohrium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Bh and atomic number 107. It is a member of the [[transition metals]] and is part of the [[7th period]] in the [[periodic table]]. Bohrium is named after the Danish physicist [[Niels Bohr]], who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 7: | ||
===Physical Properties=== | ===Physical Properties=== | ||
- '''Atomic Number''': 107 | * - '''Atomic Number''': 107 | ||
- '''Atomic Weight''': [270] (most stable isotope) | * - '''Atomic Weight''': [270] (most stable isotope) | ||
- '''Density''': Unknown, but predicted to be around 37.1 g/cm³ | * - '''Density''': Unknown, but predicted to be around 37.1 g/cm³ | ||
- '''Melting Point''': Unknown | * - '''Melting Point''': Unknown | ||
- '''Boiling Point''': Unknown | * - '''Boiling Point''': Unknown | ||
===Chemical Properties=== | ===Chemical Properties=== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 41: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
- [[Periodic Table]] | * - [[Periodic Table]] | ||
- [[Transition Metals]] | * - [[Transition Metals]] | ||
- [[Radioactive Elements]] | * - [[Radioactive Elements]] | ||
- [[Synthetic Elements]] | * - [[Synthetic Elements]] | ||
{{Bohrium}} | {{Bohrium}} | ||
| Line 59: | Line 51: | ||
[[Category:Transition metals]] | [[Category:Transition metals]] | ||
[[Category:Radioactive elements]] | [[Category:Radioactive elements]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Niels_Bohr.jpg|Niels Bohr | |||
File:Bohrium_hassium_meitnerium_ceremony.jpg|Bohrium hassium meitnerium ceremony | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:07, 23 February 2025
Bohrium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Bh and atomic number 107. It is a member of the transition metals and is part of the 7th period in the periodic table. Bohrium is named after the Danish physicist Niels Bohr, who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory.
Properties[edit]
Bohrium is a radioactive element and is not found naturally on Earth. It is produced artificially in a laboratory setting. Due to its position in the periodic table, it is expected to have properties similar to other group 7 elements, such as rhenium and manganese.
Physical Properties[edit]
- - Atomic Number: 107
- - Atomic Weight: [270] (most stable isotope)
- - Density: Unknown, but predicted to be around 37.1 g/cm³
- - Melting Point: Unknown
- - Boiling Point: Unknown
Chemical Properties[edit]
Bohrium is expected to exhibit chemical behavior similar to that of rhenium. It is predicted to form a stable +7 oxidation state, and possibly lower oxidation states as well. Due to its short half-life, detailed chemical studies have not been conducted.
Isotopes[edit]
Bohrium has several isotopes, all of which are radioactive. The most stable isotope is Bohrium-270, with a half-life of approximately 61 seconds. Other isotopes include Bohrium-267, Bohrium-271, and Bohrium-272, each with varying half-lives and decay modes.
Production[edit]
Bohrium is produced in particle accelerators through the fusion of lighter elements. The most common method involves bombarding Bismuth-209 with Chromium-54 ions:
\[ \text{\(^{209}_{83}Bi + \ ^{54}_{24}Cr \rightarrow \ ^{262}_{107}Bh + 1n\)} \]
This reaction produces Bohrium-262, which decays rapidly into lighter elements.
Applications[edit]
Due to its short half-life and the difficulty in producing it, bohrium has no practical applications outside of scientific research. It is primarily used in experiments to study the properties of superheavy elements and to test theoretical models of atomic structure.
History[edit]
Bohrium was first synthesized in 1981 by a team of scientists at the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (GSI) in Darmstadt, Germany. The team was led by Peter Armbruster and Gottfried Münzenberg. The element was named in honor of Niels Bohr, reflecting his contributions to the understanding of atomic structure.
See Also[edit]
-
Niels Bohr
-
Bohrium hassium meitnerium ceremony