Acinic cell carcinoma of the lung: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Acinic cell carcinoma of the lung | |||
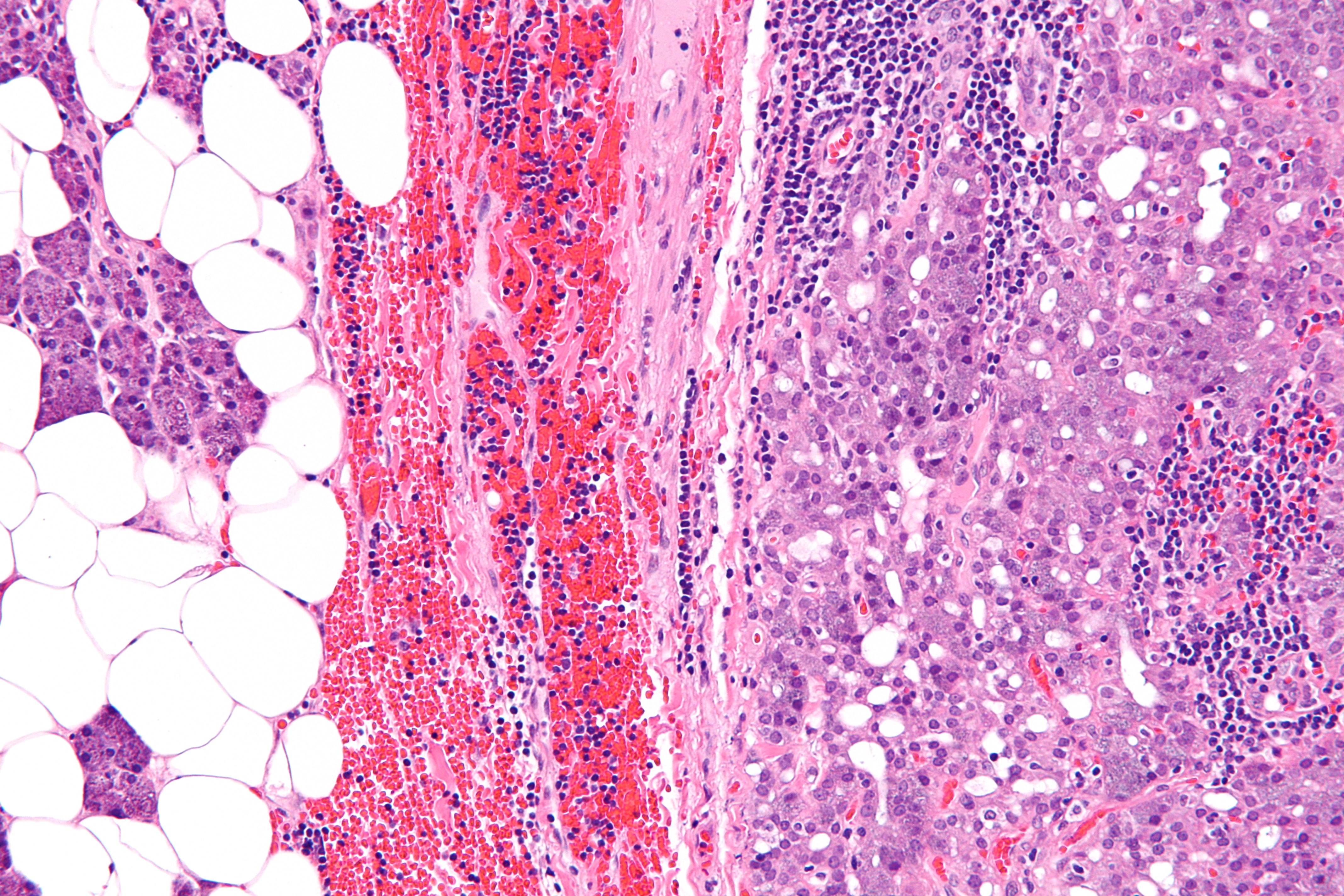
| image =[[File:Acinic_cell_carcinoma_-_high_mag.jpg|alt=Micrograph of acinic cell carcinoma, high magnification]] | |||
| caption = Micrograph of acinic cell carcinoma, high magnification | |||
| field = [[Oncology]] | |||
| synonyms = | |||
| symptoms = [[Cough]], [[hemoptysis]], [[dyspnea]] | |||
| complications = [[Metastasis]], [[respiratory failure]] | |||
| onset = | |||
| duration = | |||
| types = | |||
| causes = Unknown | |||
| risks = [[Smoking]], [[radiation exposure]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Biopsy]], [[imaging studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Adenocarcinoma]], [[mucoepidermoid carcinoma]] | |||
| prevention = | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[radiation therapy]], [[chemotherapy]] | |||
| medication = | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on stage and treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
| deaths = | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Acinic cell carcinoma - high mag.jpg|thumb|Acinic cell carcinoma - high mag]] '''Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Lung''' is a rare type of [[lung cancer]] that originates from the acinic cells, which are part of the salivary glands. This type of cancer is more commonly associated with the salivary glands, particularly the parotid gland, making its occurrence in the lung extremely rare and unusual. Due to its rarity, the understanding of acinic cell carcinoma of the lung is limited, and it is often diagnosed through histological examination, which involves studying the cells under a microscope. | [[File:Acinic cell carcinoma - high mag.jpg|thumb|Acinic cell carcinoma - high mag]] '''Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Lung''' is a rare type of [[lung cancer]] that originates from the acinic cells, which are part of the salivary glands. This type of cancer is more commonly associated with the salivary glands, particularly the parotid gland, making its occurrence in the lung extremely rare and unusual. Due to its rarity, the understanding of acinic cell carcinoma of the lung is limited, and it is often diagnosed through histological examination, which involves studying the cells under a microscope. | ||
Latest revision as of 03:40, 4 April 2025
| Acinic cell carcinoma of the lung | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Cough, hemoptysis, dyspnea |
| Complications | Metastasis, respiratory failure |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | Smoking, radiation exposure |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Adenocarcinoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on stage and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | |

Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Lung is a rare type of lung cancer that originates from the acinic cells, which are part of the salivary glands. This type of cancer is more commonly associated with the salivary glands, particularly the parotid gland, making its occurrence in the lung extremely rare and unusual. Due to its rarity, the understanding of acinic cell carcinoma of the lung is limited, and it is often diagnosed through histological examination, which involves studying the cells under a microscope.
Epidemiology[edit]
The exact incidence of acinic cell carcinoma of the lung is difficult to determine due to its rarity. It has been reported in a very limited number of case studies and medical literature, making it a challenge for researchers to provide a comprehensive epidemiological profile of this disease.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Acinic cell carcinoma is characterized by the proliferation of cells that resemble the acinar cells of the salivary glands. In the context of the lung, these cancerous cells originate from the lung tissue but mimic the appearance and behavior of salivary gland cells. The pathogenesis of acinic cell carcinoma in the lung is not well understood, partly due to its rarity.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with acinic cell carcinoma of the lung may present with symptoms similar to other forms of lung cancer, including persistent cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, and unexplained weight loss. However, due to the non-specific nature of these symptoms, the diagnosis is not straightforward and often requires a combination of imaging studies and histological examination.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of acinic cell carcinoma of the lung primarily relies on histological examination of tissue samples obtained through biopsy. Imaging studies such as CT scans and MRIs can help in identifying the presence of a mass in the lung, but a definitive diagnosis requires microscopic examination of the cancer cells.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment options for acinic cell carcinoma of the lung are similar to those for other types of lung cancer and may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the overall health of the patient, and the presence of any underlying conditions.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for acinic cell carcinoma of the lung varies depending on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed and the effectiveness of the treatment. Due to its rarity, there is limited data on the long-term outcomes for patients with this type of cancer. However, early detection and treatment are critical for improving the prognosis.
Conclusion[edit]
Acinic cell carcinoma of the lung is a rare and poorly understood type of lung cancer. Its diagnosis and treatment pose significant challenges due to its rarity and the non-specific nature of its symptoms. Further research is needed to better understand the pathogenesis, epidemiology, and optimal treatment strategies for this unusual form of lung cancer.
