WRAP53: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[Category:Human chromosome 17]] | [[Category:Human chromosome 17]] | ||
{{cancer-stub}} | {{cancer-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Figure1..png|WRAP53 | |||
File:Figure_2..png|WRAP53 | |||
File:Figure_3..png|WRAP53 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:04, 18 February 2025
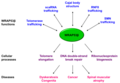
WRAP53 (WD repeat containing, antisense to TP53) is a gene that plays a crucial role in the regulation of the p53 tumor suppressor and is involved in various cellular processes, including DNA repair, telomere maintenance, and RNA splicing. The WRAP53 gene is located on human chromosome 17 and produces a protein that is essential for the proper functioning of several cellular mechanisms.
Function[edit]
WRAP53 protein is involved in directing the small Cajal body-specific RNA (scaRNA) to Cajal bodies, which are nuclear organelles involved in the modification and maturation of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs). This process is critical for the assembly of the spliceosome, a complex necessary for pre-mRNA splicing. Additionally, WRAP53 plays a vital role in the DNA damage response by facilitating the localization of the p53 protein to sites of DNA damage, thereby promoting DNA repair. It also has a function in telomere maintenance by acting as a natural antisense transcript to the telomerase RNA component (TERC), regulating telomerase activity.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Mutations or dysregulation of the WRAP53 gene have been implicated in various types of cancer, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, ovarian cancer, and breast cancer. The aberrant expression of WRAP53 can lead to the disruption of p53-mediated DNA damage response, contributing to genomic instability and cancer progression. Furthermore, due to its role in telomere maintenance, alterations in WRAP53 function can affect cellular aging and the development of age-related diseases.
Research[edit]
Research on WRAP53 is ongoing, with studies focusing on understanding its complex roles in cellular processes and its potential as a target for cancer therapy. By elucidating the mechanisms by which WRAP53 regulates p53 activity, DNA repair, and telomere maintenance, scientists aim to develop novel therapeutic strategies for treating cancers and other diseases associated with dysregulation of these pathways.
-
WRAP53
-
WRAP53
-
WRAP53