Pygidium: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
[[Category:Paleontology]] | [[Category:Paleontology]] | ||
{{biology-stub}} | {{biology-stub}} | ||
== Pygidium == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:SamGonIII_cepthopyg.png | |||
File:Trilobite_Pygidia_types.png | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:54, 17 February 2025
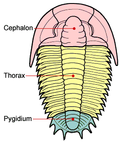
Pygidium is the terminal segment of the body in many arthropods, including insects and crustaceans. It is often considered the posterior part of the arthropod body, sometimes bearing important anatomical structures such as the anus and, in some species, the genital openings. The pygidium is particularly significant in the study of trilobites, extinct marine arthropods, where it forms part of the exoskeleton and is used in the classification and identification of fossil specimens.
Structure and Function[edit]
The structure of the pygidium varies significantly among different groups of arthropods. In trilobites, the pygidium is formed by the fusion of several body segments and is often shield-shaped, providing protection to the posterior part of the body. In modern insects, the pygidium may be less distinct but still plays a crucial role in protecting internal organs and housing the reproductive and excretory openings.
In crustaceans, such as lobsters and crabs, the pygidium is part of the tail region, which may be flexed under the body for protection or propulsion. This region is particularly important in the classification and study of these animals, as the shape and structure of the pygidium can vary widely between species.
Evolutionary Significance[edit]
The pygidium provides important clues about the evolutionary relationships between different arthropod groups. Its structure and development have been subjects of study in evolutionary biology, helping scientists understand how different arthropod lineages have diverged from common ancestors. The variation in pygidial structure among trilobites, for example, has been used extensively in the classification of these ancient creatures and in the study of their evolutionary history.
In Paleontology[edit]
In paleontology, the pygidium is a critical feature for the identification and classification of fossil arthropods, especially trilobites. The size, shape, and ornamentation of the pygidium are key diagnostic features that help paleontologists distinguish between different species and understand their evolutionary relationships. The study of pygidial variation has also provided insights into the paleoecology and behavior of these ancient organisms.
See Also[edit]