Carbon tetrafluoride: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category:Greenhouse gases]] | [[Category:Greenhouse gases]] | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Carbon_Tetrafluoride.png|Carbon tetrafluoride molecule | |||
File:Mauna_Loa_Tetrafluoromethane.jpg|Tetrafluoromethane concentration at Mauna Loa | |||
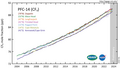
File:PFC-14_mm.png|PFC-14 molecular model | |||
File:Halogenated_gas_concentrations_1978-present.png|Halogenated gas concentrations from 1978 to present | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:34, 18 February 2025
Carbon tetrafluoride, also known as tetrafluoromethane, is a chemical compound with the formula CF4. This compound belongs to the group of perfluorocarbons (PFCs), which are compounds consisting of carbon and fluorine. Carbon tetrafluoride is a colorless, odorless, non-flammable gas at room temperature and is relatively inert. It is used in various industrial applications, including refrigeration, electronics manufacturing, and as a gas for plasma etching in semiconductor production.
Properties[edit]
Carbon tetrafluoride is a stable gas that exhibits high chemical inertness due to the strength of the carbon-fluorine bonds. It has a boiling point of -128.5°C and a melting point of -183.6°C. CF4 is slightly soluble in water but can be dissolved in some organic solvents. It is denser than air, which allows it to be collected by displacing air downwards.
Production[edit]
The production of carbon tetrafluoride involves the fluorination of carbon compounds, typically methane or carbon dioxide, using fluorine gas. The reaction with methane can be represented as: \[ CH_4 + 4F_2 \rightarrow CF_4 + 4HF \] This process requires careful control of reaction conditions to prevent the formation of unwanted byproducts.
Applications[edit]
Electronics Industry[edit]
In the electronics industry, CF4 is primarily used in plasma etching processes. Plasma etching is a critical step in the manufacturing of semiconductor devices, where CF4 plasma is used to create fine patterns on silicon wafers by selectively removing silicon or silicon compounds.
Refrigeration[edit]
Due to its low boiling point, carbon tetrafluoride has been used as a refrigerant in special applications. However, its use is limited compared to other refrigerants due to environmental concerns.
Insulating Material[edit]
CF4 is also used as an insulating material in high-voltage electrical equipment. Its inertness and non-flammability make it suitable for this application.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Carbon tetrafluoride is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential (GWP) significantly higher than that of carbon dioxide. Its long atmospheric lifetime and strong infrared absorption make it a concern for climate change. As a result, its release into the atmosphere is regulated under various international agreements.
Safety[edit]
While carbon tetrafluoride is non-toxic and non-flammable, it can act as a simple asphyxiant by displacing oxygen in the air, leading to suffocation in confined spaces. Proper ventilation and monitoring are essential when handling this gas.
See Also[edit]
-
Carbon tetrafluoride molecule
-
Tetrafluoromethane concentration at Mauna Loa
-
PFC-14 molecular model
-
Halogenated gas concentrations from 1978 to present