Log-normal distribution: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
{{Statistics-stub}} | {{Statistics-stub}} | ||
== Log-normal distribution == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Log-normal-pdfs.png|Probability density functions of log-normal distributions | |||
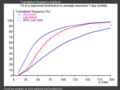
File:Log-normal-cdfs.png|Cumulative distribution functions of log-normal distributions | |||
File:Lognormal_Distribution.svg|Log-normal distribution illustration | |||
File:Probabilities_of_log_normal.png|Probabilities of log-normal distribution | |||
File:Comparison_mean_median_mode.svg|Comparison of mean, median, and mode in log-normal distribution | |||
File:LogNormal17.jpg|Log-normal distribution | |||
File:FitLogNormDistr.tif|Fitting a log-normal distribution | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:11, 18 February 2025
Log-normal distribution is a probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm is normally distributed. Thus, if the random variable X is log-normally distributed, then Y = ln(X) has a normal distribution. Equivalently, if Y follows a normal distribution, then the exponential of Y, X = exp(Y), has a log-normal distribution. This distribution is used in various fields such as finance, environmental science, medicine, and engineering to model a wide range of phenomena that are positive-valued and have skewed distributions.
Characterization[edit]
The log-normal distribution is characterized by two parameters: the mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ) of the variable's natural logarithm. These parameters correspond to the location and scale parameters of the underlying normal distribution of the logarithm of the variable.
Probability density function[edit]
The probability density function (pdf) of a log-normal distribution is given by:
\[f(x;\mu,\sigma) = \frac{1}{x\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}} \exp\left(-\frac{(\ln x - \mu)^2}{2\sigma^2}\right)\]
for x > 0, and f(x;μ,σ) = 0 otherwise. Here, μ and σ are the mean and standard deviation of the variable's logarithm, respectively.
Cumulative distribution function[edit]
The cumulative distribution function (cdf) of the log-normal distribution is:
\[F(x;\mu,\sigma) = \frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{2}\mathrm{erf}\left(\frac{\ln x - \mu}{\sigma\sqrt{2}}\right)\]
where erf is the error function.
Properties[edit]
The log-normal distribution has several notable properties:
- It is skewed to the right, with a longer tail on the right side of the mode.
- The mean, median, and mode of a log-normal distribution are different, with the relationship: mode < median < mean.
- It is bounded below by zero but has no upper bound.
- Multiplicative processes often lead to log-normal distributions due to the central limit theorem, when the logarithm of the variable is considered.
Applications[edit]
The log-normal distribution is widely used in various fields:
- In finance, it models stock prices and other financial variables that cannot be negative and are positively skewed.
- In environmental science, it describes the distribution of particle sizes, concentrations of pollutants, and other environmental data.
- In medicine, it is used to model the distribution of latency periods of diseases and the distribution of biological parameters.
- In engineering, it models failure times and loads beyond the yield point in materials.
Parameter estimation[edit]
Parameters of the log-normal distribution can be estimated using methods such as maximum likelihood estimation or the method of moments. Given a sample of n observations, the sample mean (\bar{x}) and sample standard deviation (s) of the logarithms of the observations can be used to estimate μ and σ.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />

This article is a statistics-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Log-normal distribution[edit]
-
Probability density functions of log-normal distributions
-
Cumulative distribution functions of log-normal distributions
-
Log-normal distribution illustration
-
Probabilities of log-normal distribution
-
Comparison of mean, median, and mode in log-normal distribution
-
Log-normal distribution
-
Fitting a log-normal distribution