Tert-Butylhydroquinone: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
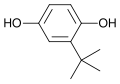
File:tert-Butylhydroquinone-Skeletal.svg|Skeletal structure of tert-Butylhydroquinone | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 22:03, 16 February 2025
Tert-Butylhydroquinone (TBHQ) is a type of aromatic organic compound that is often used as a food additive. It is a derivative of hydroquinone, substituted with a tert-butyl group.
Chemical Structure and Properties[edit]
TBHQ is a white, crystalline substance with a faint, characteristic odor. It is soluble in alcohol and ether, and practically insoluble in water. The chemical formula for TBHQ is C10H14O2, and its molecular weight is 166.22 g/mol. Its systematic name is 2-tert-butylhydroquinone.
Uses[edit]
TBHQ is widely used as a preservative for unsaturated vegetable oils and many edible animal fats. It does not cause discoloration even in the presence of iron, and does not change flavor or odor of the material to which it is added. It can be combined with other preservatives such as butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT).
Health Effects[edit]
While TBHQ is generally recognized as safe by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), it should not be consumed in large amounts. Overconsumption of TBHQ can lead to a variety of health issues, including nausea, vomiting, and in some cases, tinnitus (ringing in the ears). Long-term, high-dose exposure to TBHQ may also lead to more serious health effects, such as liver enlargement and neurotoxicity.
Regulation[edit]
In the United States, the FDA has set a limit for TBHQ to be no more than 0.02% of the oil or fat content in foods. In the European Union, TBHQ is not allowed as a food additive.
See Also[edit]
-
Skeletal structure of tert-Butylhydroquinone